Using Figure 8.3, identify each type of synovial joint by name.
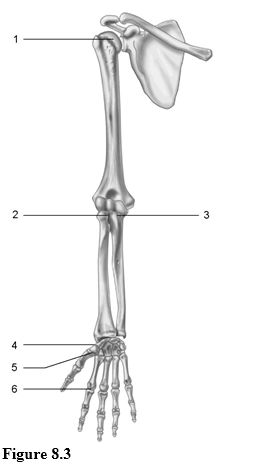
1) Joint 1.
2) Joint 2.
3) Joint 3.
4) Joint 4.
5) Joint 5.
6) Joint 6.
1) ball and socket
2) pivot joint
3) hinge joint
4) plane joint
5) saddle joint
6) condyloid joint
You might also like to view...
The most diverse tissues of the body are
A) muscle tissues. B) nervous tissues. C) epithelial tissues. D) connective tissues. E) adipose tissues.
Damage to the fovea of the eye would interfere with the ability to
A) detect objects in the periphery of ones field of vision. B) detect the detailed image of objects in the middle of ones field of vision. C) detect color images. D) regulate the amount of light striking the retina. E) focus an image.
Activity and exercise
A) keep joints functional longer. B) make joints more vulnerable to injury. C) hasten osteoarthritis. D) increase joint stiffness.
What and where is the styloid process of the ulna?
What will be an ideal response?