Discuss the applicability to mobile and ubiquitous systems of techniques drawn from the areas of
(a) peer-to-peer systems (Chapter 10); (b) coordination and agreement protocols (Chapter 15) and
(c) replication (Chapter 18).
What will be an ideal response?
This is mainly a question for class discussion but some key observations are:
(a) peer-to-peer systems are volatile but they are not necessarily physically integrated, e.g. devices involved
might be conventional PCs and typically there is no need to apply the boundary principle. Some of the p2p
algorithms assume there is a connected infrastructure.
(b) the coordination and agreement protocols are in general designed on the assumption that failure is the
exception (e.g. election algorithms) whereas in volatile systems it is the rule. Many of these techniques are too
expensive in communication or too slow to converge to be run frequently. Notions such as consensus are too
strong to implement and have to be replaced by more pragmatic, weaker abstractions such as soft state.
However, multicast provides a good level of indirection as long as relatively cheap-to-implement semantics
suffice.
(c) Chapter 15 deals with disconnected operation. However, in general the techniques considered in this
chapter tend to assume a redundancy of resources whereas in ubiquitous and mobile systems the opposite is
generally true.
You might also like to view...
One of the below programs that when called like this (with the underscore representing a digit from 1 to 4) generates this output:
``` >>> mixem_("we hold these truths") ’w.e. .h.o.l.d. .t.h.ese truths’ ```
Describe in terms of who needs access to class members why the public members should come first in a class definition.
What will be an ideal response?
Referring to the figure below, please identify the letter of the choice that best matches the numbered area on the screen.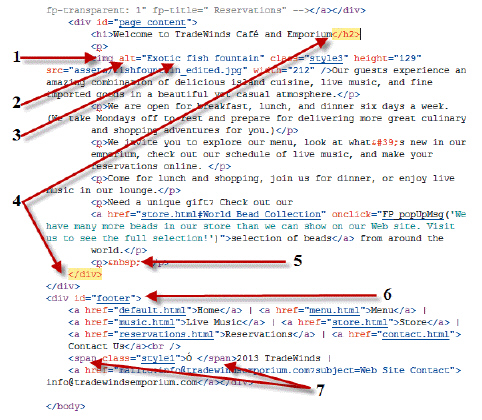
A. Element name B. Attribute name C. Attribute value D. Invalid code E. F. G. Span tag
What Active Directory partition contains the information needed to define objects and object attributes for all domains in the forest?
A. Domain directory partition B. Global catalog partition C. Schema directory partition D. Application directory partition