The U.S. dollar exchange rate, e, expressed as Japanese yen per U.S. dollar, will appreciate when:
A. the U.S. Federal Reserve eases monetary policy.
B. real GDP in the U.S. increases.
C. U.S. consumers increase their preference for Japanese cars.
D. real GDP in Japan increases.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
If a Lorenz curve for income moves rightward and becomes more bowed out over time, then
A) the population is growing. B) income is growing. C) income is being more equally distributed. D) income is being more unequally distributed.
Which of the following is not a store of value?
a. Dollar bills. b. Credit card. c. Coins. d. Gold.
The interest-rate effect
a. depends on the idea that decreases in interest rates increase the quantity of goods and services demanded. b. depends on the idea that decreases in interest rates decrease the quantity of goods and services demanded. c. is responsible for the downward slope of the money-demand curve. d. is the least important reason, in the case of the United States, for the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
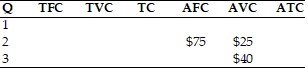 Refer to the above table. What are total fixed costs at an output of 2 units?
Refer to the above table. What are total fixed costs at an output of 2 units?
A. $150 B. $100 C. $200 D. $50