Consider an economy in long-run equilibrium with an inflation rate (?) of 0.08 per year and a natural unemployment rate of 0.05
. Suppose Okun's law holds and a one percentage point increase in the unemployment rate reduces real output by 2% of full-employment output. The expectations-augmented Phillips curve is given by
? = ?e - 2.5 (u - 0.05).
Consider a two-year disinflation. In the first year, ? = 0.06 and ?e = 0.08. In the second year, ? = 0.04 and ?e = 0.05.
(a) In the first year, what is the value of the unemployment rate?
(b) In the first year, by what percentage does output fall short of full-employment output?
(c) In the second year, what is the value of the unemployment rate?
(d) In the second year, by what percentage does output fall short of full-employment output?
(e) What is the sacrifice ratio for this disinflation?
(a) .06 = .08 - 2.5(u - .05), so u = .058.
(b) .058 - .05 = .008 = 0.8%; 0.8 × 2% = 1.6%.
(c) .04 = .05 - 2.5(u - .05), so u = .054.
(d) .054 - .05 = .004 = 0.4%; 0.4 × 2% = 0.8%.
(e) sacrifice ratio = output shortfall/change in inflation rate = (1.6% + 0.8%)/(8% - 4%) = 2.4/4 = 0.6.
You might also like to view...
According to the graph shown, the area ABC represents consumer surplus in an economy with:
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good, as well as a tariff and the world price for that good.
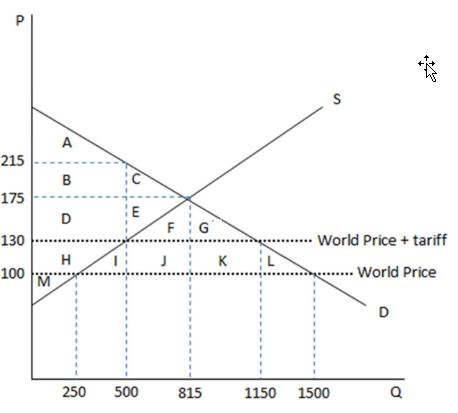
A. free trade.
B. autarky.
C. a tariff being imposed on trade.
D. None of these is true.
Consider a firm that needs one day to hire more labor, one week to increase its purchases of raw materials, and three months to change the amount of its capital. This firm's long run is
a. three months b. one week c. one day d. three months plus eight days e. three months plus one week
If a price ceiling is set at $10, and the equilibrium market price is $8, then which of the prices below is the price that consumers actually pay?
a. $2 b. $10 c. $8 d. $18
Within the Keynesian aggregate expenditures model, if the economy is below equilibrium, then there will be:
A. an increase the demand for goods and services. B. an increase in real GDP. C. lower interest rates, which will stimulate aggregate demand and keep the economy at full employment. D. a lower price level, which will quickly guide the economy to full-employment equilibrium.