The speed of a particle moving in a circle 2.0 m in radius increases at the constant rate of 4.4 m/s2 . At an instant when the magnitude of the total acceleration is 6.0 m/s2, what is the speed of the particle?
a. 3.9 m/s
b. 2.9 m/s
c. 3.5 m/s
d. 3.0 m/s
e. 1.4 m/s
B
You might also like to view...
This sequence of photos shows the Sun at one-hour intervals throughout the day of the June solstice; directions and times are indicated. Where was this photo taken?
A) the Arctic Circle B) the Antarctic Circle C) the North Pole D) the equator
A moon is in orbit around its mother planet. Which of the following statements is always true about its kinetic energy (K), and its gravitational potential energy (U)?
A) K is negative, and U is negative. B) K is negative, and U is positive. C) K is positive, and U is negative. D) K is positive, and U is positive.
Exhibit 16-1
A graph of position versus time for an object oscillating at the free end of a horizontal spring is shown below.
?
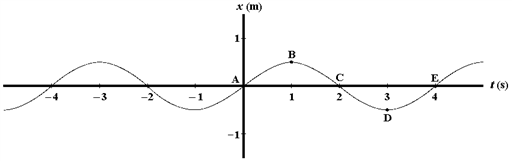
?
Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s).
Refer to . A point or points at which the object has positive velocity and zero acceleration is(are)
a.
B
b.
C
c.
D
d.
B and D
e.
A and E
Scattered light in the atmosphere is often partially polarized. The best way to determine whether or not light from a particular direction in the sky shows polarization is to
a. diffract the light through a single slit. b. squint while looking in that direction. c. rotate a piece of polaroid film about an axis parallel to the ray while looking through it in that sky direction. d. rotate a piece of polaroid film about an axis perpendicular to the ray while looking through it in that sky direction. e. reflect the rays from that direction on a shiny metal surface.