Diffraction Gratings: Monochromatic light is incident on a diffraction grating that is 75 mm wide and ruled with 50,000 lines. The second-order maximum is seen at 32.5°. What is the wavelength of the incident light?
A. 202 nm
B. 403 nm
C. 605 nm
D. 806 nm
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
An engine takes in 150 J energy from a 400 K thermal source. If the engine discharges energy into a thermal reservoir at 150K, then what is the maximum amount of work one can get out of the engine?
A. 93.8 J B. 84.2 J C. 28.5 J D. 168 J
An air-cooled low-pressure-steam condenser is shown in following figure.
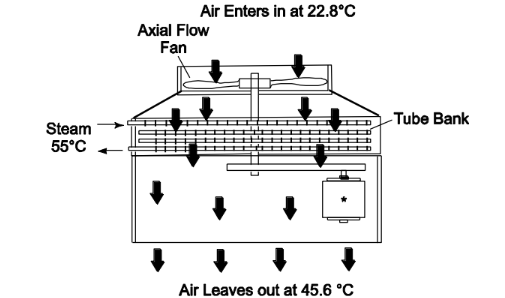
An air-cooled low-pressure-steam condenser is shown in following figure.
The tube bank is four rows deep in the direction of air flow and there are total of 80 tubes. The tubes have ID = 2.2 cm and OD 2.5 cm and are 9-m-long with circular fins on the outside. The tube-plus-fin area is 16 times the bare tube area (i.e., the fin area is 15 times the bare tube area, neglect the tube surface covered by fins). The fin efficiency is 0.75. Air flows past the outside of the tubes. On a particular day, the air enters at 22.8°C and leaves at 45.6°C. The air flow rate is 3.4 × 105 kg/h. The steam temperature is 55°C and has a condensing coefficient of 104 W/(m2 K). The steam-side fouling coefficient is 104 W/(m2K). The tube wall conductance per unit area is 105 W/(m2K). The air-side fouling resistance is negligible. The air-side-film heat transfer coefficient is 285 W/(m2K). (Note this value has been corrected for the number of transverse tube rows.) (a) What is the log-mean temperature difference between the two streams? (b) What is the rate of heat transfer? (c) What is the rate of steam condensation? (d) Estimate the rate of steam condensation if there were no fins.
GIVEN
• The condenser shown above
• Number of tubes (N) = 80 and number of rows (Nr) = 4 (in air flow direction)
• Tube diameters Di = 2.2 cm = 0.022 m Do = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Tube length (L) = 9 m
• Air temperature Ta,in = 22.8°C Ta,out = 45.6°C
• Air flow rate m a= 3.4 × 105 kg/h = 94.4 kg/s
• Steam temperature = 55°C (constant)
• Fin area = 15 (tube area)
• Fin efficiency (?f) = 0.75
• Steam side
Transfer coefficient h i= 104 W/(m2 K)
Fouling coefficient (1/Ri) = 104 W/(m2 K)
• Tube wall conductance per unit area (1/Rk) = 105 W/(m2 K)
• Air side: Transfer coefficient h o= 285 W/(m2 K)
• Fouling resistance on the air side is negligible
FIND
(a) The log-mean temperature difference(LMTD)
(b) The rate of heat transfer (q)
(c) The rate of steam condensation m
(d) Estimate the rate of steam condensation if there were no fins 2cm
ASSUMPTIONS
• Air side transfer coefficient is the same with or without fins
• Tube surface covered by the fins is negligible
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the average temperature of 34.2°C,
the specific heat (cpa) = 1013 J/(kg K),
for steam at a saturation temperature of 55°C,
the heat of vaporization (hfg) = 2600 (kJ/kg)
which of the following is true for the monuments built by ancient civilization?
A. they are based on stars. B. they are based on change in the alludes of sun during seasonal changes. C. the apex of these monuments pointed to stars. D. the geometry and architecture are based on the heavenly bodies e. all of the above
(e) A particle of mass 2m at rest decays to two identical particles each of mass m that move in opposite directions away from the decay position at a speed of 0.5.
A. C B. F