Refer to the graph below. Assume the economy is at the initial position of B2. An increase in aggregate demand with no corresponding change in inflation expectations and wage rates will tend to:
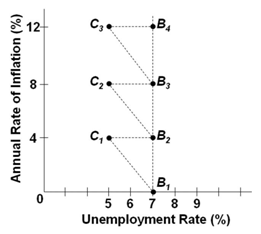
A. Temporarily move the economy to point B3
B. Temporarily move the economy to point C2
C. Temporarily move the economy to point C1
D. Have no effect in shifting the economy from point B2
B. Temporarily move the economy to point C2
You might also like to view...
The difference between the utility of expected income and expected utility from income is
A) zero because income generates utility. B) positive because if utility from income is uncertain, it is worth less. C) negative because if income is uncertain, it is worth less. D) that expected utility from income is calculated by summing the utilities of possible incomes, weighted by their probability of occurring, and the utility of expected income is calculated by summing the possible incomes, weighted by their probability of occurring, and finding the utility of that figure. E) that the utility of expected income is calculated by summing the utilities of possible incomes, weighted by their probability of occurring, and the expected utility of income is calculated by summing the possible incomes, weighted by their probability of occurring, and finding the utility of that figure.
An example of a final good is:
A. chocolate chips purchased by Nabisco to make Keebler chocolate chip cookies. B. chocolate chips purchased by you to make chocolate chip cookies. C. chocolate chips purchased by a restaurant to make a chocolate chip cookie pie to sell. D. chocolate used to make Cocoa Rice Krispies.
Suppose the actual federal funds rate is below the rate implied by a particular inflation goal. In this situation, the Taylor rule implies that
A) monetary policy is expansionary.
B) monetary policy is contractionary.
C) monetary policy is neither expansionary or contractionary.
D) fiscal policy is contractionary.
The primary objective of most central banks in industrialized economies is:
A. low unemployment. B. high securities prices. C. price stability. D. a strong domestic currency.