If the cost of capital decreases the isocost line will
A) stay the same.
B) shift outward in parallel fashion.
C) rotate outward around the point where only labor is employed in production.
D) shift inward in parallel fashion.
C
You might also like to view...
A flat wage profile refers to
A) wage compression. B) backloaded compensation. C) an efficiency wage. D) deferred compensation.
Which of the following is true of perfect competition but is not true of monopolistic competition?
a. The firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve. b. The firm faces a downward-sloping marginal revenue curve. c. The firm will earn zero economic profit in the long run. d. The firm will produce at a point where price equals marginal cost.
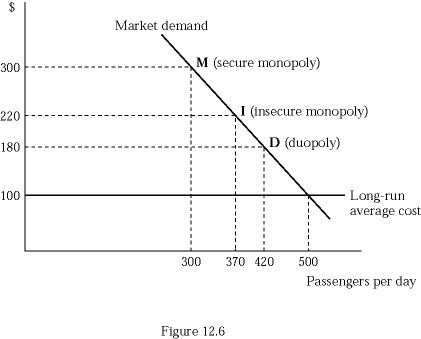 In Figure 12.6, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit maximizing price of $300 per ticket. Suppose that Fly Smart discovers that a second airline is contemplating entering the market. If the minimum market entry quantity is 130 passengers per day, what is Fly Smart's profit when it commits to the entry-deterring quantity?
In Figure 12.6, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit maximizing price of $300 per ticket. Suppose that Fly Smart discovers that a second airline is contemplating entering the market. If the minimum market entry quantity is 130 passengers per day, what is Fly Smart's profit when it commits to the entry-deterring quantity?
A. $60,000 B. $44,400 C. $33,600 D. $29,600
Economies and diseconomies of scale explain
A. the distinction between fixed and variable costs. B. why the firm's short-run marginal cost curve cuts the short-run average variable cost curve at its minimum point. C. why the firm's long-run average cost curve is U-shaped. D. the profit-maximizing level of production.