The aggregate demand curve slopes downward due to the:
a. Phillips-Curve effect, wealth effect, and net export effect.
b. Productivity effect, income effect, and real money supply effect.
c. Real money supply effect, wealth effect, and net export effect.
d. Productivity effect, income effect, and Gibson paradox.
e. Purchasing power effect, real money supply effect, wealth effect, and real goods effect.
.C
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below, the economy is initially at point A on the monetary policy reaction function (RF1) and the aggregate demand curve (AD1). The actual rate of inflation is ?' and the Federal Reserve's target inflation rate is ?*1. 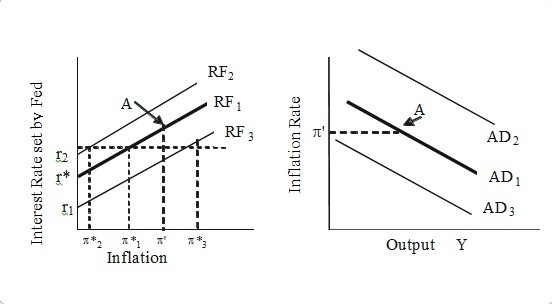 If the Federal Reserve lowers its target inflation rate to ?*2, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will ________ and the aggregate demand curve will ________.
If the Federal Reserve lowers its target inflation rate to ?*2, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will ________ and the aggregate demand curve will ________.
A. shift to RF3; shift to AD2 B. shift to RF2; shift to AD2 C. shift to RF2: shift to AD3 D. shift to RF3: shift to AD3
According to the government budget constraint, any excess of public expenditures and transfers over taxes and user fees must be funded by
A) private borrowing. B) government borrowing. C) U.S. Treasury money creation. D) Federal Reserve money creation.
GDP per capita is a relatively good measurement of:
a. the distribution of income. b. purchasing power. c. household production. d. the standard of living.
Season ticket holders often purchase their tickets before a season begins. There is often a discount associated with season tickets. Why?
A) Buying season tickets entails risk, which consumers are willing to bear if they are compensated for doing so. B) Buying season tickets is a way of guaranteeing a supply of tickets for the secondary market. C) Selling season tickets entails greater transactions costs which team owners hope to avoid. D) Sports teams are local monopolies.