Passive continental margins are commonly associated with volcanic and earthquake activity.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
False
You might also like to view...
The hydronium ion concentration in an aqueous solution where the pH = 5 equals
A. 1 × 10-5 M. B. 1 × 10-3 M. C. 1 × 10-7 M. D. 1 × 10-9 M.
Compute the gradient of the outer base of the Okmok Caldera along line EF. Use the coastline closest to Point E as the starting point for measuring horizontal distance, and the northwest rim of the caldera as the stopping point. It may be easiest to use the graphic map scale to measure out a distance of four or five miles, and then determine the elevation change over that distance.
The following questions are based on Map T-2, the “Umnak, Alaska,” topographic map (scale 1:250,000; contour interval 200 feet). In this problem, you will estimate the height of the original Okmok volcano before the caldera was formed. (You may also determine the elevation changes and distances needed to make these calculations by using Google Earth™.)
Gradients can be used to estimate an elevation increase over a given distance. (See Exercise 34 for a review of gradients.) For example, if a mountain has a gradient of 1000 feet per mile, we can estimate that over a horizontal distance of five miles, the elevation will increase by 5000 feet.
5 miles * 1000 ft>mi = 5000 foot elevation increase over five miles
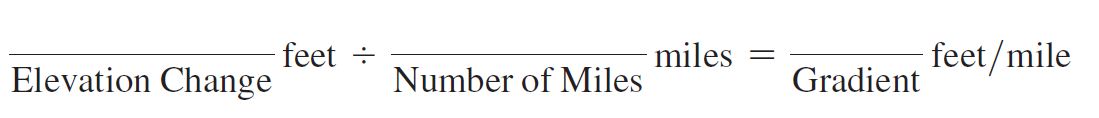
What type of continental margin is presently represented by the eastern edge of North America? How did it form?
What types of sedimentation is this margin experiencing? What will be an ideal response?
What is a shadow zone?
a. A zone that is unable to be penetrated by sound waves due to the density of seawater b. A zone that is unable to be penetrated by light waves due to deep depths c. A zone in front of ships and submarines that creates a converging blind spot for sound waves d. A zone where the divergence of sound waves creates a region that has little sound energy penetration e. A zone that is unable to be penetrated by light waves due to high scattering