What is Gross Domestic Product? What is included in this statistic? What is excluded? Give two examples of goods or services that are included in GDP and two examples of goods or services that are excluded
Gross Domestic Product is an aggregate and therefore an abstraction. It is the sum of the money values of all final goods and services produced in the domestic economy during a specific time period, usually a calendar quarter or year. GDP excludes goods and services produced in another quarter or year and it excludes intermediate goods and services. It includes final goods and services produced in the United States, regardless of the ownership of the facility producing the goods or services. It excludes goods and services produced outside the United States, even if they are produced by subsidiaries or branches of U.S. firms. GDP includes only goods and services that are bought and sold in organized markets. Examples of items included in GDP are anything newly produced in the specified time period. It is important that the item be produced in the period and not "new" items that may have been in storage or inventory for a long time before being sold. Items excluded from GDP are any intermediate good or service, any used good, any good or service produced outside the United States, and any good or service that does not pass through an organized market.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as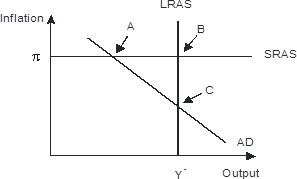
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
All of the following will cause a shift in the supply of jeans EXCEPT
a. a decrease in the prices of jeans. b. a decrease in the number of jean manufacturers. c. an increase in the cost of producing jeans. d. a per-unit government subsidy on the production of jeans.
Which of the following is likely to increase the equilibrium real interest rate?
a. greater tax benefits for IRAs b. technological improvement creating profitable investment opportunities c. elimination of an investment tax credit for corporations d. an increased consumption tax
In the analysis of educational spending on outcomes, it is generally the case that
A. spending on raising teacher salaries and reducing class size matters. B. only the spending on reducing class size matters. C. neither higher salaries nor reduced class size matters. D. only the spending devoted to raising teacher salaries matters.