If an amount "$AAA" today earns interest at a rate of "i"% per year, then the accumulated amount at the end of "n" years will be:
A. $AAA × n × i
B. $AAA × in
C. ($AAA)n × (1 + i)
D. $AAA × (1 + i)n
D. $AAA × (1 + i)n
You might also like to view...
When there is a decrease in labor supply, real wages are likely to
A) remain the same. B) decrease. C) increase. D) allow less leisure time.
The median voter must have preferences that reflect those of all people in the community.
A. True B. False C. Uncertain
Which of the following elements of the federal income tax code are not indexed for inflation?
A. The standard deduction B. The brackets C. The personal exemption D. All of these elements are indexed.
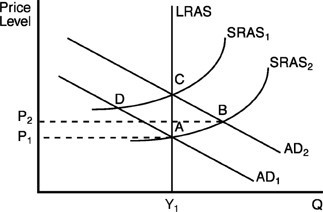 In the above figure, if A is the initial equilibrium point and there is an unanticipated rise in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2, then
In the above figure, if A is the initial equilibrium point and there is an unanticipated rise in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2, then
A. the new short-run equilibrium will be at point B. B. the new long-run equilibrium will be at point B. C. real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per year will fall below Y1. D. the new short-run equilibrium will be at point D.