Below, the graph on the left shows long-run average and marginal cost for a typical firm in a perfectly competitive industry. The graph on the right shows demand and long-run supply for an increasing-cost industry.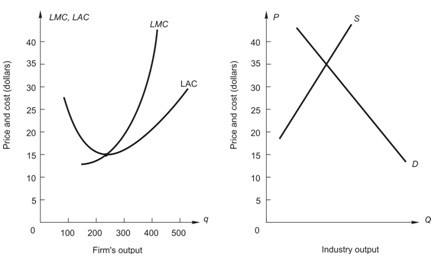 If this were an increasing cost industry, what would be the price when the industry gets to long-run competitive equilibrium?
If this were an increasing cost industry, what would be the price when the industry gets to long-run competitive equilibrium?
A. $35
B. between $35 and $15
C. below $15
D. above $35
E. $15
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Opportunity cost is defined as the
A) total value of all the alternatives given up B) highest-valued alternative given up C) cost of not doing all of the things you would like to do. D) lowest-valued alternative given up
A local restaurant offers an "all you can eat" ribs special. You pay $11.95, and then you can eat as many servings as you desire at no additional cost. It would follow that you will stop eating when:
a. your marginal utility (or value) derived from eating another serving is zero. b. your total utility (or value) derived from all of the servings consumed just equals $11.95. c. your marginal utility (or value) derived from another serving equals $11.95. d. it is physically impossible for you to eat any more.
Which of the following is assumed to be constant along a per-worker production function?
a. Output per worker b. Capital per worker c. Level of technology d. Amount of capital e. Amount of output
Lenders generally want a higher interest rate to compensate them when loans stretch over a longer period because:
A. the opportunity cost increases over time. B. there's more uncertainty about potential future investment opportunities. C. lenders want to be compensated for being unable to get their money back quickly. D. All of these are true.