Double markup problems arise when
a. upstream firms have market power
b. downstream firms have no market power
c. upstream and downstream products are unrelated in demand
d. upstream and downstream firm's pricing decisions tend to increase the demand for the other product
a
You might also like to view...
Potential GDP is also referred to as
A) full-employment GDP. B) politico-economic GDP. C) realized GDP. D) balanced-budget GDP.
An example of physical capital is a:
A. seeds. B. bank loan. C. plow. D. tree.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 the result in the long run would be: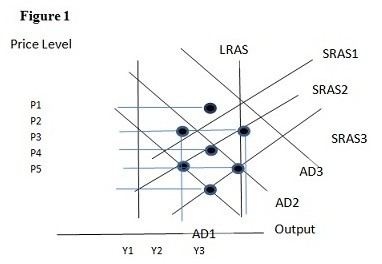
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y2. C. P3 and Y1. D. P2 and Y3.
Refer to the graph below, where Sd and Dd are the domestic supply and demand curves for a product. The world price of the product is $6. If the economy is open to international trade but a per unit tariff of $4 is imposed, then the total revenue going to domestic producers would be:
A. $400, the total revenue (after tariff) going to foreign producers would be $120, and the tariff revenue going to the government would be $80 B. $240, the total revenue (after tariff) going to foreign producers would be $240, and the tariff revenue going to the government would be $80 C. $400, the total revenue (after tariff) going to foreign producers would be $240, and the tariff revenue going to the government would be $80 D. $240, the total revenue (after tariff) going to foreign producers would be $120, and the tariff revenue going to the government would be $120