If the demand for a good does not change, how will an increase in the price of that good affect the consumer surplus from it?
What will be an ideal response?
The consumer surplus equals the difference between the marginal benefit of the good and its price summed over the quantity consumed. If the demand for a good does not change, then the marginal benefit of that good does not change. Hence an increase in the price decreases the consumer surplus from that good because 1 ) it decreases the quantity purchased, and 2 ) it decreases the consumer surplus on each particular unit that is purchased.
You might also like to view...
If the local cable TV company is a natural monopoly and required by regulators to set its price equal to marginal cost, it makes zero profit and produces the efficient level of output
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
What are the key differences between how we illustrate an expansionary fiscal policy in the basic aggregate demand and aggregate supply model and in the dynamic aggregate demand and aggregate supply model?
What will be an ideal response?
What does it mean for a producer to internalize an? externality?
A. The producer is prohibited from producing products which generate externalities. B. The producer must find ways to address externality problems which extend beyond geographic borders. C. The producer is limiting outsourced production. D. The producer is forced to factor into production costs the cost of the externalities created in their production of output.
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.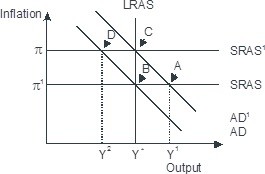
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary