A consumer's real disposable income equals
A) wage income plus consumption expenditures.
B) wage income plus profit income minus taxes.
C) total income minus profit income minus taxes.
D) total income minus wage income minus taxes.
B
You might also like to view...
Why does the government intervene in the market for research, especially medical research?
What will be an ideal response?
Halifax & Smyth (H&S) is a clothier that specializes in expensive men's suits, and the firm makes the suits from wool fabrics that are woven by one of the firm's divisions
This division is not the only source for this material, and H&S could buy or sell wool fabric in the outside competitive market. H&S will buy some of the wool fabric that it needs for suits from the outside market if the: A) market price is less than the optimal transfer price if the outside market did not exist. B) market price is less than the point where the net marginal revenue of weaving wool fabric intersects the marginal cost of wool fabric. C) market price is less than the point where the net marginal revenue of assembling men's suits intersects the marginal cost of assembly. D) Both A and B are correct.
The game in the figure shown is a version of:
This figure shows the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.
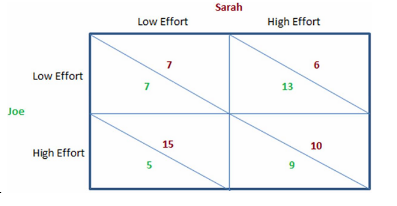
A. the prisoner's dilemma.
B. the first-mover advantage.
C. a sequential game.
D. a repeated game.
When all markets are in simultaneous equilibrium, the general equilibrium condition has been satisfied.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)