Discuss the historic increases and decreases in unionism in the United States and how it affects current labor relations today
Unions are no longer as important as they used to be with only 13 percent of American workers belong to unions. This percentage is about half of what it was in the heyday of unionism in the mid-1950s. In 1930, unions had enrolled slightly less than 7 percent of the U.S. labor force, and by 1933 this figure had slipped to barely more than 5 percent. Membership peaked in the 1950s but since then the unionization rate has fallen with few interruptions. One reason unionization in the United States has been declining is the shift of the U.S. labor force into service industries and out of manufacturing. In addition, American workers' preferences seem to have shifted away from unions. The increasing share of women in the labor force may have contributed to this trend, because women have traditionally been less prone than men to join unions. Finally, American unions came under increasing pressure in the 1990s and early 2000 . because of stronger competition both at home and abroad. In response, firms closed plants and eliminated jobs. This "downsizing" trend made it even more difficult for unions to win concessions that improve the economic positions of their members which has reduced the attractiveness of union membership.
You might also like to view...
The aggregate demand curve shifts when any of the following factors change EXCEPT
A) monetary policy. B) fiscal policy. C) the price level. D) expectations about the future. E) foreign income.
With a temporary income tax surcharge, according to the ________, household consumption should ________
A) PIH; fall as disposable income falls B) PIH; rise since the decrease is disposable income is temporary C) LCH; fall since disposable income over the lifecycle falls D) None of the above is correct since a temporary change affects neither permanent income or relative lifecycle earnings.
For the perfectly competitive firm shown in Figure 9-6,
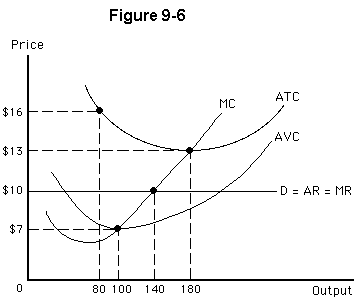
a.
profit rises when the firm raises its price and lowers its output
b.
the profit-maximizing output level is 180 units
c.
an economic loss occurs at the profit-maximizing output level
d.
the profit-maximizing output level is 100 units
e.
the firm will earn short-run profits
Answer the following questions true (T) or false (F)
1. A university must decide if it should stop offering foreign language classes. This decision involves answering the economic question of "how to produce." 2. In market economies, income distribution is always going to be completely equitable. 3. "An increase in the price of gasoline will increase the demand for hybrid vehicles." This statement is an example of a positive economic statement.