Money is
a. an asset that is widely accepted as a means of payment in the economy
b. any asset that is convertible into cash
c. an asset that is backed by a precious metal such as gold or silver
d. any financial asset created and issued by government
e. anything used to pay for goods and services, including currency, checks, and credit cards
A
You might also like to view...
Employing Figure 3-1 above, autonomous consumption expenditures are ________, and the marginal propensity to consume is ________
A) 200; 0.75 B) 500; 1 C) 200; 0.60 D) 0; 1
The equation illustrating leakages equal injections in an economy would be:
a. I + S + NT = G + S b. G + S = C + I + X c. S + NT + M = I + G + X d. I + G + X = Rent + Wages + Profits + Interest
Sulfur Dioxide Discharged (Tons)Firm AFirm B10$8,000$9,000910,00012,000815,00018,000720,00027,000628,00037,000Table 16.3Table 16.3 shows the production cost for two utilities at different levels of sulfur dioxide emissions. Assume that the government issued 8 marketable pollution permits to each firm and that Firm A has sold one permit to Firm B. If Firm B wants to purchase a second permit to be able to discharge 10 tons of sulfur dioxide, what is Firm B's willingness to pay?
A. $2,000 B. $3,000 C. $5,000 D. $9,000
If the government set a price floor at $18
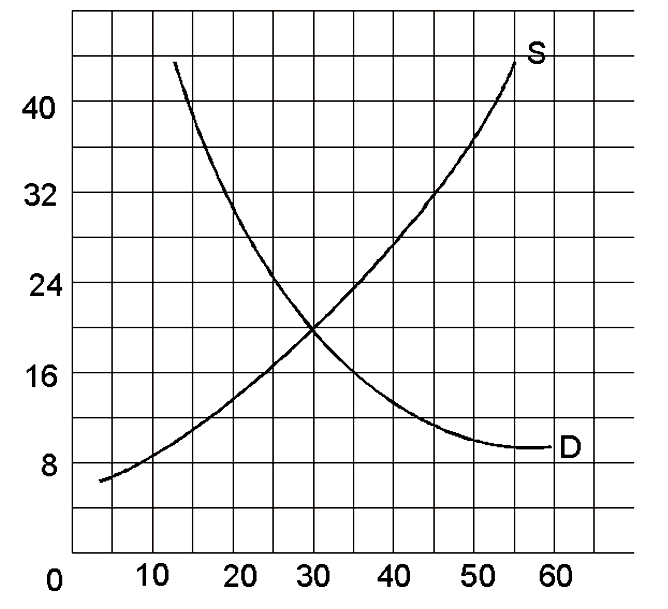
A. there would be a temporary surplus, then prices would fall to equilibrium.
B. the price floor would not have any effect on this market.
C. then quantity demanded would be greater than quantity supplied.
D. there would be a permanent surplus, at least until the price floor was lifted.