What's the dominant strategy for each firm?
a. Charge a low price
b. Charge a high price
c. Firm A charge a low price and firm B charge a high price
d. Firm A charge a high price and firm B charge a low price
a
You might also like to view...
The distribution of income in the United States is characterized by the following relationship between the mean, median, and mode incomes
A) mean income < median income < mode income. B) mode income < median income < mean income. C) median income < mean income < mode income. D) mode income < mean income < median income.
The net factor income from the rest of the world (NFIFA) appears in the Irish Balance of Payments as:
(a) A credit item in the current account; (b) A debit item in the current account; (c) A debit item in the capital account; (d) A debit item in the financial account.
With an increase in government purchases financed by an increase in the marginal tax rate on labor income, the change in labor supply depends on whether the:
a. negative substitution effect is bigger than the positive income effect. b. positive substitution effect is bigger than the negative income effect. c. negative substitution effect is bigger than the negative income effect. d. positive substitution effect is bigger than the positive income effect.
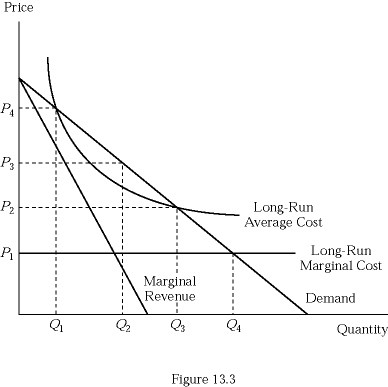 If price were regulated to be equal to long-run marginal cost, the firm in Figure 13.3 would be:
If price were regulated to be equal to long-run marginal cost, the firm in Figure 13.3 would be:
A. making a zero economic profit. B. losing money. C. making a positive economic profit. D. breaking even.