A. How are marginal cost and marginal benefits related to total cost and total benefit curves? Illustrate your answer using carefully labeled diagrams. B. Illustrate the optimal choice of an activity using both a total cost and total benefit curve diagram and a MC and MB curve diagram.
What will be an ideal response?
Marginal cost at an activity level X* is measured by the slope of the total cost curve at X*:
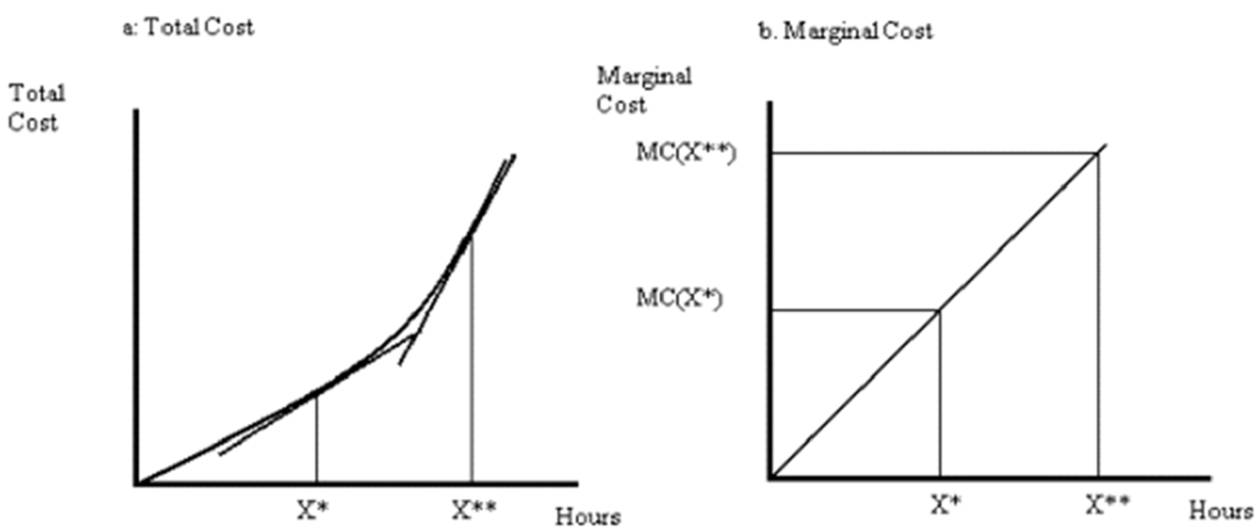
Since the slope of the line tangent to the total cost curve at X** is steeper than that at X*, MC is greater at X** then it is at X*. Similarly, marginal benefit is measured by the slope of a line tangent to the total benefit curve:
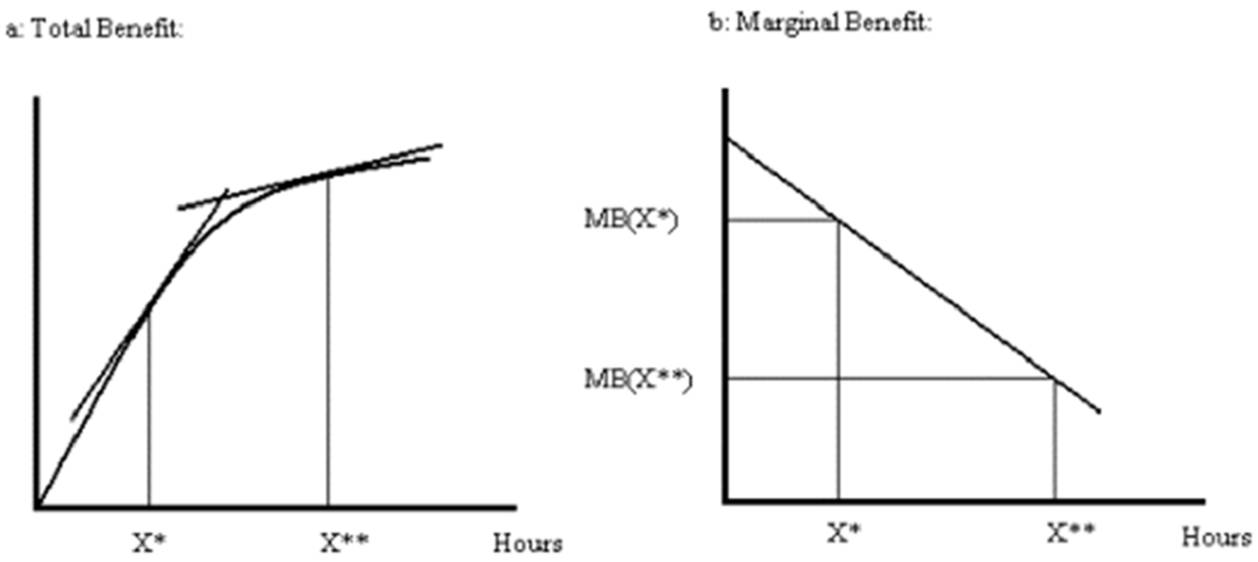
Since the slope of the line tangent to the total benefit curve at X** is less steep than that at X*, MB at X** is less than MB at X*.
You might also like to view...
In the basic closed-economy ISLM model, the money market can be described by the
A) money demand function. B) money supply. C) money market equilibrium condition. D) all of the above.
1. Money market mutual funds held by individuals 2. Savings deposits, including money market deposit accounts 3. Money market mutual funds held by businesses 4. Currency held by the public 5. Small time deposits 6. Checkable deposits Refer to the list above. The M1 money supply is composed of items:
4 and 6 1 and 4 5 and 6 6 and 7
Suppose that the cross price elasticity of demand between goods A and B equals 1.25. Which of the following is TRUE?
A. Goods A and B are complements because the cross price elasticity is positive. B. Goods A and B are substitutes because the cross price elasticity is greater than one. C. Goods A and B are substitutes because the cross price elasticity is positive. D. Goods A and B are complements because the cross price elasticity is greater than one.
According to the rational expectation hypothesis, unpredictable shocks may cause
A. sustained levels of unemployment. B. uncontrollable inflation. C. long-lasting recession. D. disequilibrium in the labor market.