Suppose Frank quits his $25,000 a year job and starts his own hauling company. He takes $10,000 out of his savings account at the bank, where he was earning 5 percent interest, to buy a truck. His other expenses, including the truck, are $20,000 . Frank's revenues are $48,000 . Frank ends up with
a. $3,000 in wage-related rent
b. $2,500 in entrepreneurial profit
c. a $7,000 loss
d. $48,000 in entrepreneurial profit
e. $3,000 in entrepreneurial profit
B
You might also like to view...
The small but non-trivial costs that a firms incurs when changes product prices are also called
A) menu costs. B) price inertia. C) sticky costs. D) sunk costs.
If the government accelerates money supply growth and enlarges the budget deficit to stimulate aggregate demand, the rational expectations hypothesis indicates that decision makers will:
a. ignore the policy until it exerts an observable impact on prices, output, and employment. b. quickly take steps to adjust their decision making in light of the more expansionary policies. c. be fooled at the outset but eventually adjust their decision making in accordance with the change in policy. d. be unaware that this policy change has been implemented until a higher rate of inflation is observed.
The total utility from consuming five muffins is 14, 24, 35, 43, and 50 utils, respectively. Marginal utility begins to diminish after consuming the first muffin
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the graph shown. The profit-maximizing monopolist produces output: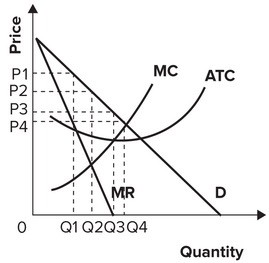
A. Q1. B. Q2. C. Q3. D. Q4.