Countries do not in fact export the goods the H.O. theory predicts. Discuss
What will be an ideal response?
This statement is not true. Although one may find many cases where it seems to be true (e.g., the Leontief Paradox), all one needs to do in order to render the above statement not (generally) true is to find one counter example. In fact, one can find large subsets of agricultural and commodity products in which the H.O predictions are generally fulfilled. Labor-intensive countries such as Bangladesh do in fact export relatively labor-intensive goods. Capital-intensive countries such as Germany do in fact export capital-intensive products (at least to South countries). Countries such as Costa Rica ("sunshine abundant") tend to export bananas (sunshine-intensive products). The U.S. (a wheat-land-abundant country) does indeed export wheat (a wheat-land intensive product). In fact, since the early 1980s, the Leontief Paradox was not found to describe the U.S. trade data (hence ratifying the H.O. theory).
You might also like to view...
When the use of a communally owned resource has no price, then people will
A. use too much of this resource. B. use less of the resource than usual. C. use another resource altogether. D. not use this resource.
Which of the following should not be counted in a cost-benefit analysis?
a. direct benefits and costs b. real secondary benefits c. technological secondary costs d. pecuniary benefits e. intangibles
What is the difference in the quantity of coffee demanded in Quahog when the price changes from $4 per pound to $3 per pound?
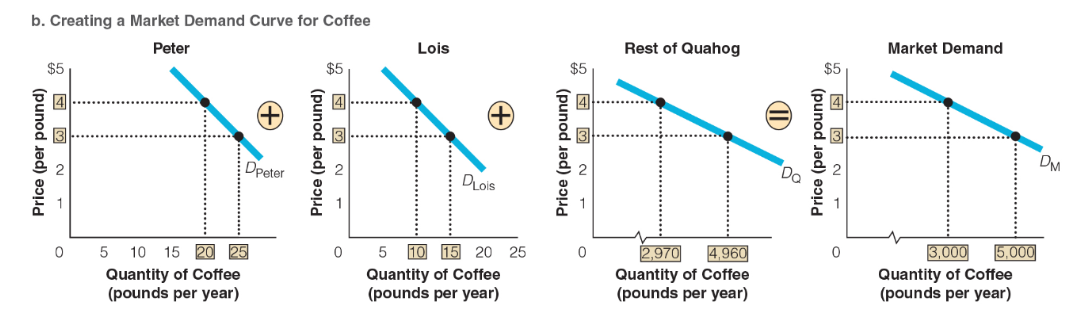
a. The quantity decreases by 1,990 pounds per year.
b. The quantity increases by 1,990 pounds per year.
c. The quantity decreases by 2,000 pounds per year.
d. The quantity increases by 2,000 pounds per year.
If unions are successful in negotiating a wage higher than the market equilibrium wage, and also guarantee employers that they can hire as many labor hours as they desire per week at the union wage,
A. the quantity of labor demanded will exceed the quantity supplied at the union wage. B. the quantity of labor demanded will equal the quantity supplied at the union wage. C. the quantity of labor demanded will fall short of the quantity supplied at the union wage. D. all workers who join the union will be guaranteed a job.