For model M1, suppose you choose the cutoff threshold to be t = 0.5. In other words, any test instances whose posterior probability is greater than t will be classified as a positive example. Compute the precision, recall, and F-measure for the model at this threshold value.
You are asked to evaluate the performance of two classification models, M1
and M2. The test set you have chosen contains 26 binary attributes, labeled
as A through Z.
Table 5.5 shows the posterior probabilities obtained by applying the models to
the test set. (Only the posterior probabilities for the positive class are shown).
As this is a two-class problem, P(?)=1 ? P(+) and P(?|A, . . . , Z)=1 ?
P(+|A, . . . , Z). Assume that we are mostly interested in detecting instances
from the positive class.
When t = 0.5, the confusion matrix for M1 is shown below.
![]()
Precision = 3/4 = 75%.
Recall = 3/5 = 60%.
F-measure = (2 × .75 × .6)/(.75 + .6) = 0.667.
You might also like to view...
When a relational expression is false, it has the value
a. 1 b. 0 c. 0, 1, or -1 d. -1 e. None of these
A power supply is rated in for each level
A) Volts; amperage B) Amps; voltage C) Farads; capacitance D) Ohms; resistance
FIGURE WD 7-1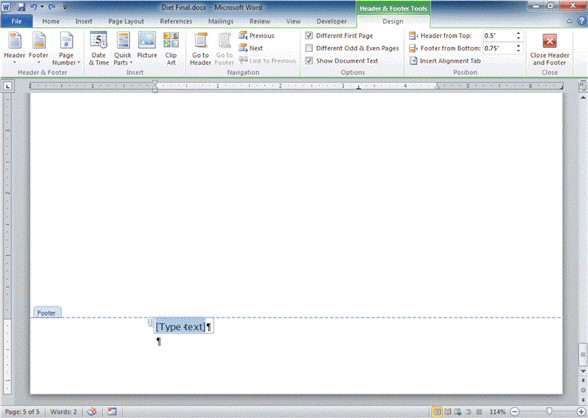 Referring to Figure WD 7-1 above, the entry with the words "Type text" is a ____ control.
Referring to Figure WD 7-1 above, the entry with the words "Type text" is a ____ control.
A. footer B. header C. content D. placeholder
If an HTML document wants to access its parent frameset, it can do so by using the parent object. If that page needs to access the parent frameset of its own parent, it can use two instances of the JavaScript ____ object.
A. parent B. child C. either a. or b. D. neither a. nor b.