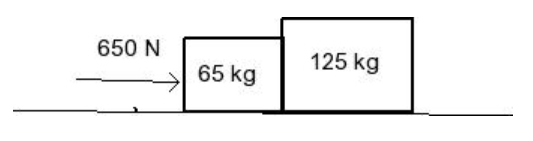
Two crates of mass 65 kg and 125 kg are in contact and at rest on a horizontal surface (figure below). A force of 650 N is exerted on the 65 kg crate. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.18, calculate:
a) the acceleration of the system and
b) the force that each crate exerts on the other. Draw a FBD (full body diagram). Show all work.
Answer:
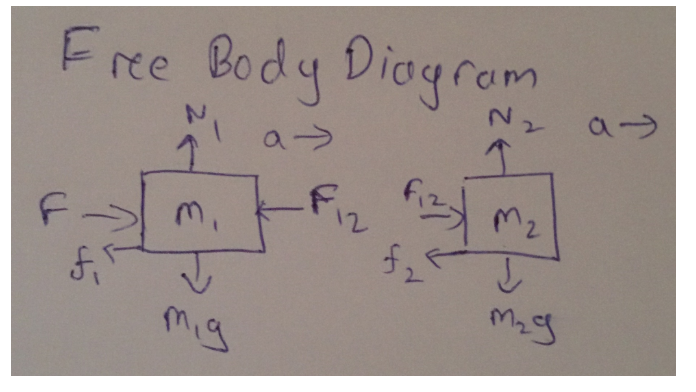
Gravitational acceleration = g = 9.81 m/s2
Mass of the first crate = m1 = 65 kg
Mass of the second crate = m2 = 125 kg
Force acting on the crates = F = 650 N
Coefficient of kinetic friction = \mu = 0.18
Acceleration of the system = a
Force exerted by the crates on each other = F12
Normal force on the first crate = N1
Friction force on the first crate = f1
Normal force on the second crate = N2
Friction force on the second crate = f2
From the free body diagram,
In the vertical direction for the first crate,
m1g = N1
f1 = \muN1
f1 = \mum1g
In the vertical direction for the second crate,
m2g = N2
f2 = \muN2
f2 = \mum2g
In the horizontal direction for the first crate,
m1a = F - F12 - f1
F12 = F - f1 - m1a
In the vertical direction for the second crate,
m2a = F12 - f2
m2a = F - f1 - m1a - f2
(m1 + m2)a = F - \mum1g - \mum2g
(m1 + m2)a = F - \mug(m1 + m2)
(65 + 125)a = 650 - (0.18)(9.81)(65 + 125)
a = 1.655 m/s2
F12 = F - f1 - m1a
F12 = F - \mum1g - m1a
F12 = 650 - (0.18)(65)(9.81) - (65)(1.655)
F12 = 427.648 N
a) Acceleration of the system = 1.655 m/s2
b) Force that crates exert on each other = 427.648 N
You might also like to view...
What is the approximate diameter of the Milky Way Galaxy in light-years?
A. 100 B. 10 C. 100,000 D. 1,000,000 E. 1,000
An equal amount of 0°C air that is twice as hot has a temperature of
A) 0°C. B) 64°C. C) 100°C. D) 273°C. E) none of the above
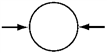
Pairs of forces of equal magnitude act on identical cylinders as shown in the figures. In which example is the cylinder in translational and rotational equilibrium?
A.
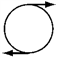
B.
C.
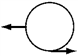
D.
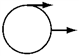
E.
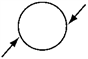
The cosmic background radiation
a. has a blackbody spectrum. b. has its peak emission in the microwave band. c. corresponds to a blackbody at a temperature of 2.726 kelvins. d. all of the above