Suppose you are offered a gamble in which you win $1,000 1/3 half the time but lose $800 2/3 half the time. If you are risk lover will you take the gamble? What will your expected payoff be?
What will be an ideal response?
The expected payoff would be:
1/3 (+$1,000 ) + 2/3 (-$800 ) = -$200.
From this calculation, we know that risk-neutral individuals would not take the gamble, but it is not clear what a risk-loving individual would do.
You might also like to view...
Assume a small nation has the following statistics: its consumption expenditure is $15 million, investment is $2 million, government expenditure on goods and services is $1 million, exports of goods and services to foreigners is $1 million, and
imports of goods and services from foreigners is $1.5 million. Calculate this nation's GDP.
In the case of unemployment compensation why would the benefits received principle of taxation not be entirely practical? Explain
What will be an ideal response?
A temporary decrease in government purchases causes the real interest rate to ________ and output to ________ in the short run, before prices adjust to restore equilibrium
A) rise; rise B) rise; fall C) fall; rise D) fall; fall
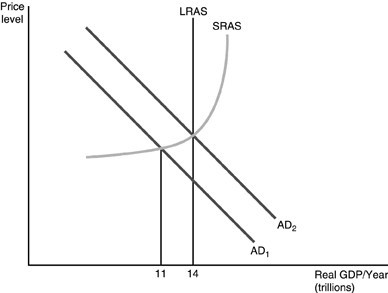 Refer to the above figure. The government has just engaged in expansionary fiscal policy shifting the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2. Interest rates have started to rise. Which of the following statements is TRUE in the short run?
Refer to the above figure. The government has just engaged in expansionary fiscal policy shifting the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2. Interest rates have started to rise. Which of the following statements is TRUE in the short run?
A. Real GDP will fall back to $11 trillion since the effect that increased government spending has on real GDP is short lived. B. Real GDP will end up somewhere between $11 and $14 trillion as businesses and consumers reduce their spending in response to the increase in interest rates. C. Real GDP will go beyond $14 trillion as businesses and consumers react to the increase in interest rates. D. Real GDP will be $14 trillion since the effect of government spending is not influenced by interest rates.