Government-imposed quantitative limits on the amount of pollution firms are allowed to produce is an example of
A) the Pigovian method of pollution control.
B) a command-and-control approach to pollution reduction.
C) a Coasian solution to pollution reduction.
D) a tradable emission allowance system of pollution control.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 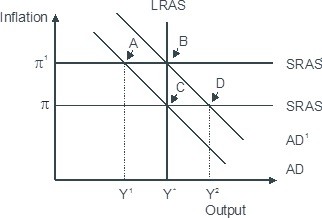
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
Low wages and poor working conditions in many U.S. trade partners
A) prove that the gains-from-trade arguments of the Ricardian model are false. B) may be a fact of life, but economists don't care. C) are facts emphasized by U.S. labor in its contract negotiations. D) prove that the gains-from-trade arguments of the Ricardian model are true. E) prove that international trade is exploitative.
If no fiscal policy changes are made, suppose the current aggregate demand curve will increase horizontally (shift rightward) by $1,000 billion and cause inflation. If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.90, federal policymakers could follow Keynesian economics and restrain inflation by decreasing:
a. government spending by $100 billion. b. taxes by $100 billion. c. taxes by $1,000 billion. d. government spending by $1,000 billion.
An example of an oligopoly is: a. the restaurant industry. b. the wheat market
c. the cigarette industry. d. the beef industry.