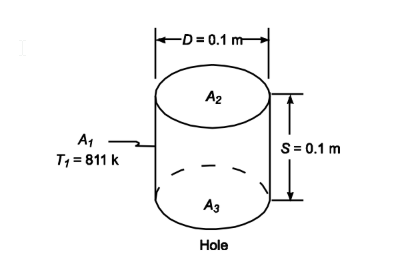
A large slab of steel 0.1-m-thick contains a 0.1-m-diameter circular hole, whose axis is normal to the surface. Considering the sides of the hole to be black, specify the rate of radiative heat loss from the hole. The plate is at 811 K, the surroundings are at 300 K.
GIVEN
• A large slab of steel with a hole whose axis is normal to the surface
• Slab thickness (S) = 0.1 m
• Hole diameter (D) = 0.1 m
• Plate temperature (T1) = 811 K
• Temperature of surrounding (T?) = 300 K
FIND
• The rate of radiative heat loss from the hole (qr)
ASSUMPTIONS
• The sides of the hole are black
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
for
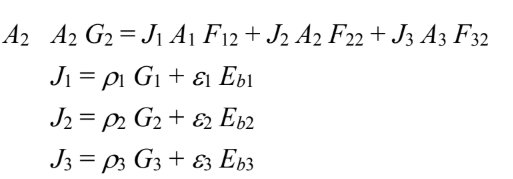
Since all surfaces behave as blackbodies
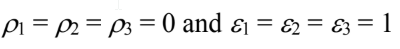
Therefore
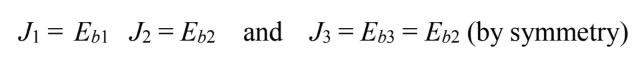
Substituting these into the above equation yields
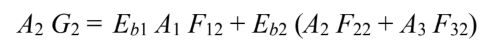
Since A2 cannot see itself F22 = 0

By symmetry F12 = F13
The sum of the shape factors from one surface must be unity
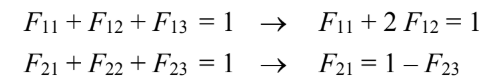
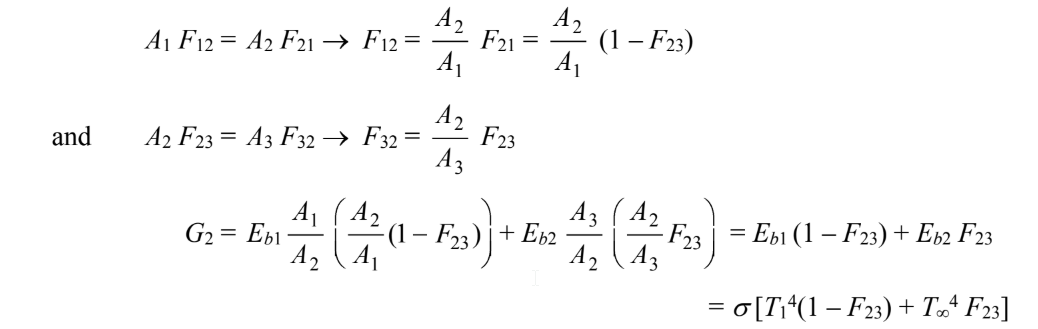
The shape factor F23 can be determined for D/S = 0.1 m/0.1 m = 1.0, and for disks with direct radiation, curve 1 applies and the shape factor F23?0.19.
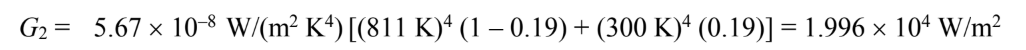
The rate of heat transfer through A2 is
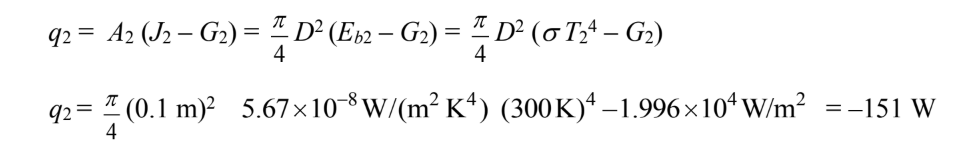
The negative sign indicates net heat loss through A2. By symmetry, the total energy leaving the hole is
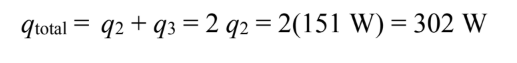
You might also like to view...
Where in Venus's atmosphere are sulfuric acid clouds found?
A. at very high altitudes B. everywhere in the atmosphere C. near the surface, like fog D. There are no sulfuric acid clouds on this planet.
The solar constant is a measure of:
A) the energy received by the Sun on Earth's surface. B) the energy received by the Sun at the location of Earth. C) the energy received by the Sun at any location in the solar system. D) the energy emitted by the Sun at the photosphere. E) the total energy emitted by the Sun in all directions.
A child is riding a tricycle. The pedals are attached directly to the front wheel, which has a radius of 13 cm. The rear wheels are smaller, and have a radius of 8.0 cm
If the child is pedaling at 16 rpm, what is the angular speed of the rear wheels? A) 15 rpm B) 26 rpm C) 24 rpm D) 20 rpm E) 50 rpm
Each choice below describes how a few astronomical phenomena are related to time periods. Which list is entirely correct? (Careful: some lists are partially correct.)
A) Earth's rotation defines a day. The saros cycle of eclipses defines a month. Earth's orbit defines a year. Earth's cycle of axis precession takes 26,000 years. B) Earth's rotation defines a day. The cycle of the Moon's phases takes about a month. Earth's orbit defines a year. Earth's cycle of axis precession takes 26,000 years. C) Earth's rotation defines a day. The cycle of the Moon's phases takes about a week. Earth's orbit defines a year. Earth's cycle of axis precession defines a month. D) Earth's rotation defines a day. The Sun's rotation defines a week. The Moon's rotation defines a month. Earth's orbit defines a year.