When a price-taking country joins the global market for some good, it:
A. shifts the world demand and supply to the right.
B. has a negligible effect on the world equilibrium.
C. shifts the world demand to the right, and the world supply to the left.
D. shifts the world demand and supply to the left.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suppose that in each of four successive years producers sell more of their product and at lower prices. This could be explained
A. by small annual increases in demand. B. as an exception to the law of supply. C. in terms of a stable supply curve and increasing demand. D. in terms of a stable demand curve and increasing supply.
The marginal revenue product of labor is
a. how much labor can be purchased with the revenue from the sale of one more unit of the good b. how much the marginal revenue changes when you add more labor c. the same as the marginal revenue product of capital when the markets for labor and capital are in equilibrium d. determined by the wage rate e. the contribution to total revenue made by the marginal laborer
The more differentiated the product,
A. the more elastic the demand. B. the more inelastic the demand. C. the more the entire demand curve shifts right. D. the more the entire demand curve shifts left.
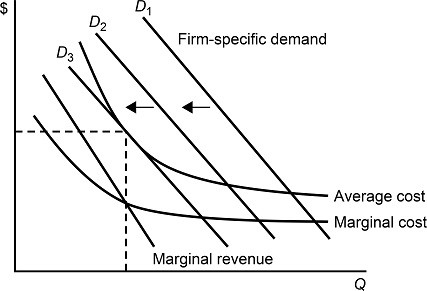 Figure 11.3Figure 11.3 shows demands and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. When the firm's demand curve shifts from D1 to D2 and to D3, in the long run we would expect:
Figure 11.3Figure 11.3 shows demands and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. When the firm's demand curve shifts from D1 to D2 and to D3, in the long run we would expect:
A. the firm to earn a zero economic profit. B. the firm to charge a price equal to its marginal cost. C. the firm to increase its output level. D. the firm to produce at the lowest average cost.