Refer to Figure g. Lily's benefit function (dashed) is more concave than Millie's benefit function (dotted). Lily:
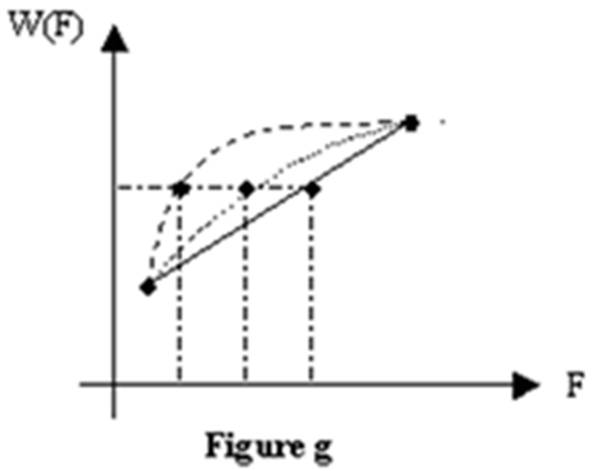
B. is less risk averse than Millie.
C. has a smaller risk premium than Millie.
D. has a larger certainty equivalent than Millie.
A. is more risk averse than Millie.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following are examples of perfectly competitive markets?
A) Wheat B) Textiles C) Gold D) The stock market E) all of the above
Alex must prepare for exams in both biology and economics this week. Assume that the production possibilities curve showing the tradeoff between exam scores in biology and economics is concave toward the origin. As Alex moves along the curve spending more of his time studying for economics, the opportunity cost of an hour of preparation for economics: a. increases
b. remains constant. c. decreases. d. first increases then decreases.
In a December 2007 New York Times column, Paul Krugman noted that
a. it is difficult to find instances of trade between high-wage countries in the modern era. b. it is difficult to find instances of trade between high-wage countries and low-wage countries in the modern era. c. the United States now imports more oil and other raw materials from other advanced countries than from the third world. d. the United States now imports more manufactured goods from the third world than from other advanced countries.
If a firm faces a flat demand curve,
A) it cannot engage in price discrimination. B) it can only engage in two-part tariffs. C) it can only engage in perfect price discrimination. D) None of the above.