Explain the relationship between the aggregate expenditures model in graph (A) below and the aggregate demand–aggregate supply model in graph (B) below. In other words, explain how points 1, 2, and 3 are related to points 1’, 2’, and 3’.
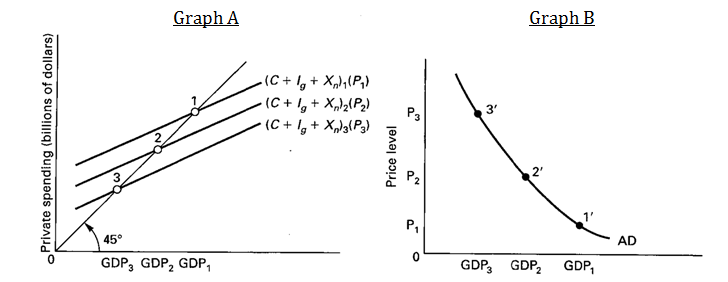
Through the real-balances, interest-rate, and foreign purchases effects, the consumption, investment, and net exports schedules and therefore the aggregate expenditures schedule will rise when the price level declines and fall when the price level increases. If the aggregate expenditure schedule is at (C + Ig + Xn)2 when the price level is P2, we can combine that price level and the equilibrium output, GDP2, to determine one point (2’) on the aggregate demand curve. A lower price level such as P1 shifts aggregate expenditures to (C + Ig + Xn)1, providing us with point 1’ on the aggregate demand curve. Similarly, a higher price level at P3 shifts aggregate expenditures down to (C + Ig + Xn)3 so P3 and GDP3 yield another point on the aggregate demand curve at 3’.
You might also like to view...
What will happen to the demand curve for workers in steel mills if some technology that increases their productivity is introduced assuming all else equal?
A) It will cause a downward movement along the demand curve of the workers. B) It will cause an upward movement along the demand curve of the workers. C) It will cause a leftward shift in the demand curve of the workers. D) It may cause a rightward shift in the demand curve of the workers.
In a market economy, buyers and sellers communicate their intentions to one another through:
a. government planners. b. negotiations overseen by government agencies. c. elected officials. d. prices.
Which of the following represents the amount of income that is actually available to people for consumption and saving?
a. Net national product b. National income c. Disposable personal income d. Gross national product e. Personal income
Tariffs increase equilibrium price and quantity.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)