Write a program that accepts a string as input, then prints out the vowels in that string and then prints the consonants in that string.
This is simply a matter of combining justvowels and notvowels:
```
def splitem(name):
vowels= ""
consonants = ""
for letter in name:
if letter.lower() in "aeiou":
vowels = vowels + letter
if letter.lower() in "qwrtypsdfghjklzxcvbnm":
consonants = consonants + letter
print "Vowels: "+vowels
print "Consonsants: "+consonants
```
Note: This version explicitly checks for consonants, instead if a character is not a vowel.
A version in which that line is replaced with: if not letter.lower() in "aeiou": would also
be acceptable.
You might also like to view...
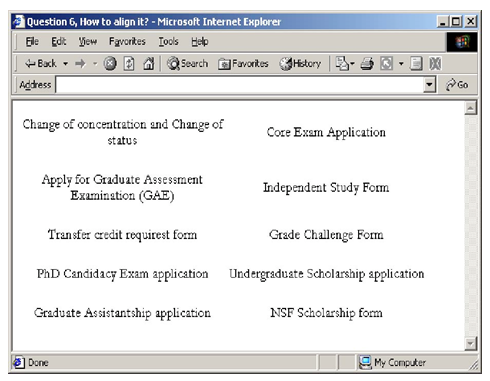
Figure 5-21 is an example that’s not well aligned. Explain what you would do to improve the alignment. It may be helpful to create a photocopy of the example and draw on it.
The proper sequence of steps needed to correct invalid statements and reexecute a program is:
a. Enter the editor, make corrections, link the program, reload the program, and save the program. b. Enter the editor, compile, load the program, correct statements, link the program, and save the program. c. Enter the editor, insert corrected statements, load, compile, and execute the program. d. Enter the editor, correct invalid statements, save the program, compile, link, load, and execute the program. e. none of the above
________ are copies of files and folders that Windows automatically saves as part of a restore point?
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Which of the following are mandatory access controls embedded in object and subject properties?
A. Object capabilities B. Security labels C. Access control lists D. Whitelists