Statistically, midlife does not bring about an increase in:
A. depression.
B. suicide.
C. divorce.
D. all of these answers are correct.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following theories of deviance is LEAST associated with sociobiology?
A) intelligence theory: low intelligence leads to deviant and criminal behavior B) social learning theory: we learn deviance from our peers C) XYY" theory: the extra Y chromosome in males causes criminal behavior D) body type theory: people with muscular bodies are prone to be criminals
Adults with a(n) __________ attachment style shun or evade emotional closeness
a. avoidant b. insecure/anxious c. secure d. ambivalent
The variable FECHLD is best described as:
Figure 7.1
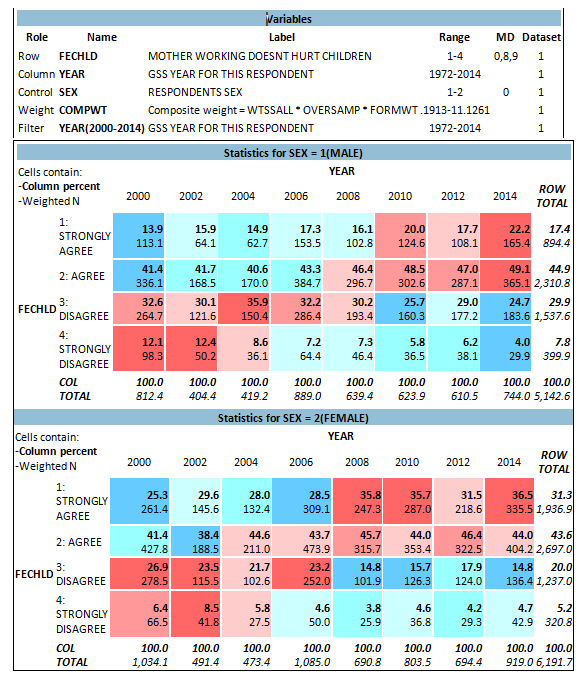
A team of researchers is interested to know whether beliefs about working mothers are related to respondents’ gender, and how these beliefs have changed over recent years. They make a cross-tab of FECHLD by YEAR, using SEX as a control variable. The variable FECHLD corresponds to the survey question, “Please tell me whether you strongly agree, agree, disagree, or strongly disagree with it… A working mother can establish just as warm and secure a relationship with her children as a mother who does not work.”
a. a dummy variable.
b. a categorical variable.
c. an ordinal variable.
d. an interval-ration level variable.
Why do religious economists believe that competition among secular viewpoints and many religions leads to increased participation in religion in modern societies?
a. Competition makes each religious group try harder to win followers, and the presence of numerous religions means that there is likely to be something for just about everyone. b. Competition against secularism has shown that religious viewpoints have better explanatory power for life's basic problems. c. Religions that see themselves as in competition with one another are more likely to evolve into secular-style beliefs. d. Modern societies need multiple religions competing for the economy to function, providing untaxed incentives for belief.