The low saving rate in the United States is no cause for concern, so long as people in other countries are saving and are willing to send their savings into the U.S. economy by buying our assets. Comment
What will be an ideal response?
Capital inflow does help to sustain investment in the U.S. above what it would be otherwise. But having savers in other countries finance our investment means that they own a portion of the resulting economic growth, leaving less for U.S. citizens to enjoy. Because capital inflow is an increase in the supply of savings, it can lower the return and thus incentive to save, discouraging U.S. citizens from ever consuming less and saving more. Capital inflow, also, may reflect a global imbalance in which the combination of high consumer demand and low return on saving fuels speculative activities (e.g., housing boom). As long as U.S. citizens consume so much and save so little, our trade deficit and corresponding indebtedness to other economies will persist.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. What is the Nash equilibrium of this game? 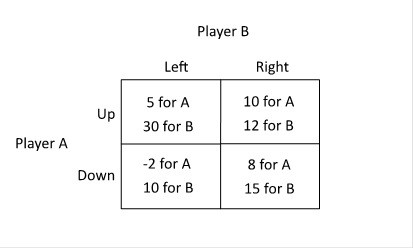
A. A chooses Up, B chooses Right B. A chooses Up, B chooses Left C. A chooses Down, B chooses Left D. A chooses Down, B chooses Right
Other things equal, the demand for a good tends to be more inelastic when
a. there are fewer available substitutes. b. a longer time period is considered. c. the good is considered a luxury good. d. the market for the good is more narrowly defined.
What is the change in the money supply when the Fed purchases $700 worth of bonds and the required reserve ratio is 14 percent assuming banks hold no excess reserves?
Which one of these firms would be a monopolistic competitor?
A. AT&T B. A local phone company C. A Tex-Mex restaurant in San Antonio, Texas D. The only used car dealer within 300 miles of Livingston, Montana