Average total cost is ______.
a. how much it costs to produce one unit of output
b. the mean sum needed to buy one unit of output
c. the variable input costs that change with output
d. the cost changes resulting from a change in output
a. how much it costs to produce one unit of output
You might also like to view...
There is a negative relationship between the real rate of interest and investment spending
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Describe how Mexico's development strategy changed from the 1950s to today and how that changed the production location decisions of firms
What will be an ideal response?
Price can be written as P = 155 - Q. (A) TR is price multiplied by quantity for TR = P × Q = 155 × Q - (0.25) × Q 2 . Marginal revenue is MR = 155 - 2 × Q d . Marginal costs are MC = 110 - 0.5 × Q. MC = MB for monopolist Q* = 30, P* = 125, TR = P × Q = 125 × 30 = 3,750 Profits = TR - TC = 3,750 - [110 × 30 - (0.25) 30 2 ] = 675. (B) AC = TC/Q = 110 + (0.25) × Q. AC = D if the government intervenes, 110 - (0.25) × Q = 155 - Q so Q* = 60 and P* = 95 TR = P × Q = 60 × 95 = 5,700 Profits = TR - TC = 5,700 - [110 × 60 - (0.25) × 60 2 ] = 0 (C) Now the monopolist produces at perfectly competitive market quantity, S = D so MC = D thus 110 + (0.5) × Q = 155 - Q Q* = 90 and P* = 65 TR = P × Q = 65 × 90 = 5,850 Profits = TR - TC = 5,850 - [110 × 90 - (0.25) × 90 2 ] = - 2,025
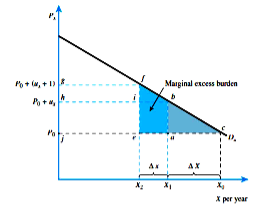
(A) If the original price of the good was $10 and a $4 tax was imposed, what is the tax
income? What is the excess burden?
(B) How much marginal excess burden will be created if an additional dollar of tax is levied?
(C) How much additional tax is collected?
Exchanges of stocks take place
A. in the principle financial city of each country, such as New York City for the United States and London for England. B. in a decentralized fashion around the world. C. in New York City only. D. in centralized physical locations known as stock exchanges and online through Internet brokers.