Table 1.3 shows the hypothetical trade-off between different combinations of brushes and combs that might be produced in a year with the limited capacity for Country X, ceteris paribus.Table 1.3Production Possibilities for Brushes and CombsCombinationNumber of combsOpportunity Cost(Foregone brushes)Number of brushesOpportunity Cost (Foregone combs)J4 0NAK3 10 L2 17 M1 21 N0NA23 On the basis Table 1.3, what is gained by producing at point M rather than point N?
A. 2 combs.
B. 23 combs.
C. 1 comb.
D. 21 combs.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
At a given output level, a monopolist earns a profit only if the
a. slope of its TR curve exceeds the slope of his TC curve. b. height of its MR curve exceeds the height of his MC curve. c. height of its demand curve exceeds the height of his MR curve. d. height of its demand curve exceeds the height of his ATC curve.
Exhibit 8-2 Demand and cost information for a monopoly Q P TC 0 40 10 1 30 15 2 20 25 3 10 40 4 0 60 The marginal revenue of the second unit of output in Exhibit 8-2 is:
A. 10. B. 20. C. 30. D. 40.
The economy was initially in equilibrium at point 3 and interest rates increased by 4 percentage points because of government deficit financing. The public spending, however, improves business confidence and activity that exactly offsets the potential crowding-out effect. This situation would result in a new equilibrium at point:
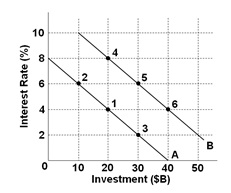
Refer to the above graph.
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Autonomous consumption is
A. that part of consumption that rises or falls with changes in disposable income. B. the minimum that people will spend even if disposable income is zero. C. the amount people will spend when the C line crosses the 45-degree line. D. the amount people will spend when income is equal to consumption.