Assume that the inner cylinder in Problem 7.40 is a heat source consisting of an aluminum-clad rod of uranium, 5-cm-OD and 2-m-long. Estimate the heat flux that raises the temperature of the bismuth 40°C and the maximum center and surface temperatures necessary to transfer heat at this rate.
GIVEN
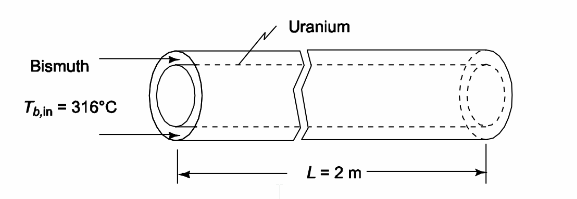
Liquid bismuth flowing through an annulus
Annulus inside diameter (Di) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Annulus outside diameter (Do) = 6.1 cm = 0.061 m
Bismuth velocity (V) = 4.5 m/s
Bismuth temperature (Tb) = 316°C
Inner cylinder is an aluminum clad uranium heat source
Cylinder length (L) = 2 m
From Problem 7.40: c h
26,800 W/(m2 K)
FIND
(a) The heat flux (QG/At) necessary to raise the bismuth temperature 40°C, and
(b) The maximum center (Tu,o) and surface (Tu,ro) temperatures of the uranium
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
The Bismuth temperature given is the bulk Bismuth temperature
Thermal resistance of the aluminum is negligible
Thickness of the aluminum is negligible
SKETCH
(a) The rate of heat transfer required to raise the Bismuth by 40°C is
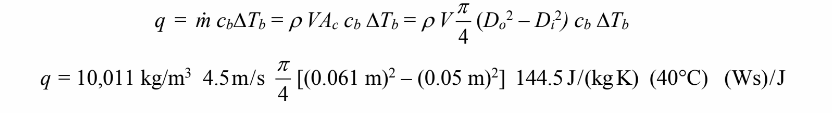
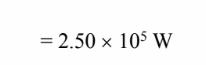
Therefore, the average heat flux is
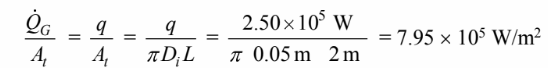
The temperature difference between the uranium and bismuth (?Tub) required to transfer this heat can
be calculated from

The maximum uranium surface temperature will occur at the outlet where the bismuth temperature is
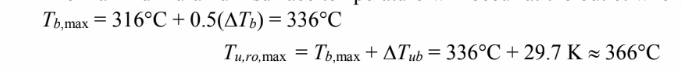
The rate of internal heat generation per unit volume is
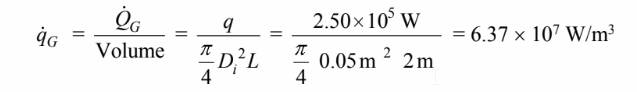
The maximum temperature at the center of the uranium is given
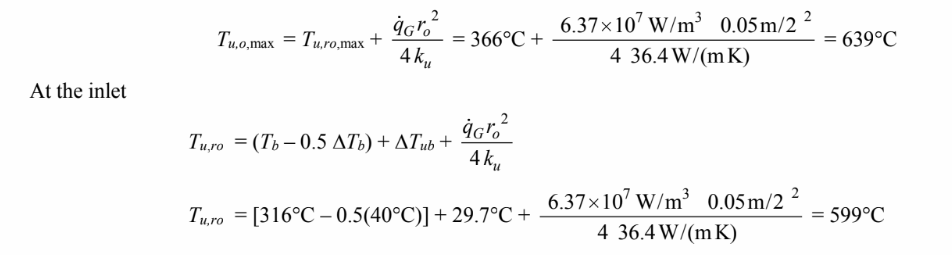
Therefore, the average uranium temperature is approximately
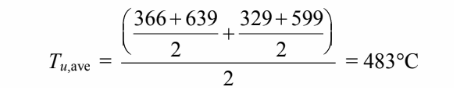
Repeating the calculation using the thermal conductivity of uranium evaluated at this temperature
yields the following result

You might also like to view...
Planes traveling between Seattle and Tokyo often go near Alaska because
A) the distance is shorter. B) there is less air traffic to contend with. C) planes travel faster in cooler air. D) the plane can stay over the safety of land for longer.
You are given two converging lenses to build a compound microscope. Lens A has focal length 0.50 cm and lens B has focal length of 3.0 cm. Which one of the two lenses would you use for the objective?
A) Lens A, because it has the shorter focal length. B) Lens B, because it has the longer focal length. C) It makes no difference which lens I use for the objective. D) None, because the objective should be a diverging lens.
The jovian planets:
A) all lie less than 5 AU from the Sun. B) all have rings around their equators. C) all spin slower than the Earth. D) have satellite systems with less than 4 moons. E) are all much more dense than any of the terrestrials planets.
Which particle was the last to be discovered?
a. electron b. neutrino c. neutron d. proton