As we saw in the chapter, some financial instruments are used primarily to transfer risk. Explain how a bread maker can use a financial instrument to transfer the following risk: the bread maker has the opportunity to provide bread to a local army base. The base figures they will need 10,000 loaves of bread each week, or roughly 500,000 for a year. The problem is the baker must quote a price for the entire year. The baker would really like to have this contract but he realizes that fluctuating input prices (specifically wheat) could result in significant losses.
What will be an ideal response?
The baker could quote a price for bread based on today's price and then purchase wheat a futures contract for wheat at today's price, for delivery one year from now. If actual wheat prices do increase the baker will lose money on the actual baking operations but these losses will be offset by the profits he will earn on the wheat futures contract. If wheat prices end up decreasing, he will suffer losses on the futures contract but will offset these by having higher profits from baking. In this case the futures contract accomplishes exactly what it was supposed to do. It transferred the risk of volatile wheat prices from the baker, who otherwise wouldn't accept the opportunity to provide bread at a guaranteed price for a year, to someone who was more willing to accept this risk.
You might also like to view...
Perfect price discrimination is when a firm can charge each customer exactly what they are willing to pay.
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
Which of the following conditions is not required for price discrimination?
A. The seller must possess some degree of monopoly power. B. Buyers with different elasticities must be physically separate from each other. C. The good or service cannot be resold by original buyers. D. The seller must be able to distinguish buyers with different elasticities of demand.
What are some of the ways a private group can overcome a free rider problem?
What will be an ideal response?
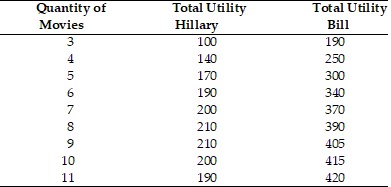 According to the above table, Hillary's marginal utility from watching the 5th movie is
According to the above table, Hillary's marginal utility from watching the 5th movie is
A. 170 units of utility. B. 20 units of utility. C. 30 units of utility. D. 50 units of utility.