Describe and explain a perfectly competitive firm's short-run supply curve.
What will be an ideal response?
A perfectly competitive firm's short-run supply curve is the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above the minimum of its average variable cost curve. A profit-maximizing firm will always produce a quantity such that price is equal to marginal cost, provided that the price of the product is high enough so that it can cover its variable costs and at least part of its fixed costs. This means that price must exceed the minimum of average variable cost. Thus, by using the part of the marginal cost curve that lies above the minimum of average variable cost, we can determine the quantity that a firm will produce at every given price. This is precisely what the firm's supply curve is.
You might also like to view...
If the quantity supplied stays the same no matter what the price is, then supply is
A) perfectly inelastic. B) perfectly elastic. C) unit elastic. D) undefined.
Refer to the accompanying figure. At a price of $3, there will be: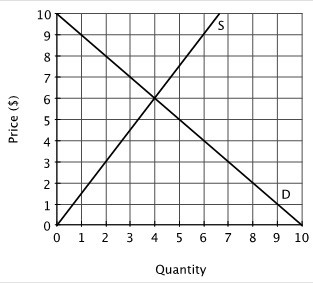
A. an excess demand of 7 units. B. an excess supply of 7 units. C. an excess demand of 5 units. D. an excess supply of 2 units.
According to Keynesians, an increase in the money supply will have its greatest impact on GDP when the aggregate demand curve intersects:
A. the vertical portion of the aggregate supply curve. B. the upward sloping portion of the aggregate supply curve. C. the horizontal portion of the aggregate supply curve. D. either the upward sloping or the vertical portions of the aggregate supply curve.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1) Asymmetric information in the health care market has increased the supply of health care. 2) A moral hazard problem arises in the health care market because health insurance encourages people to overconsume health care. 3) Insurance companies use deductibles and copayments to control increases in the amount of health care demanded. 4) Because employer payments for health insurance are not subject to income or payroll taxes, government in effect provides a subsidy to health care.