Sound of frequency 600 Hz is emitted by a point source. The sound can travel along two different paths to reach an observer
What is the minimum non-zero path length difference that results in constructive interference? Assume the speed of sound in air is 340 m/s.
A)
28.3 cm
B)
1.13 m
C)
1.76 m
D)
88.2 cm
E)
56.7 cm
E
You might also like to view...
Which of the four labeled arrows in this photo of the full moon is point to one of the lunar maria?
A) Arrow 1 B) Arrow 2 C) Arrow 3 D) Arrow 4
How would the atmospheric temperature structure differ from the generic structure if a planet had a reasonably thick atmosphere but no ultraviolet-absorbing gases? Which of the terrestrial planets have this structure?
What will be an ideal response?
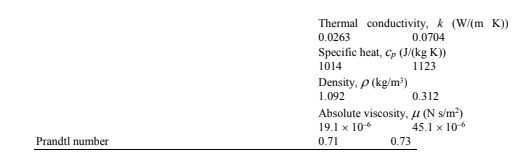
A 1.2-kg mass is projected up a rough circular track (radius = 0.80 m) as shown. The speed of the mass at point A is 8.4 m/s, and at point B, it is 5.6 m/s. What is the change in mechanical energy between A and B caused by the force of friction?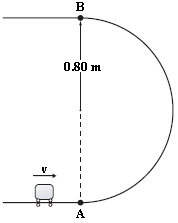
A. ?2.7 J B. ?8.8 J C. ?4.7 J D. ?6.7 J E. ?19 J
Calculate the overall heat transfer coefficient and the rate of heat flow from the hot gasses to the cold air in the cross flow tube-bank of heat exchanger shown in the accompanying illustration for the following operating conditions
Air flow rate = 0.4 kg/s.
Hot gas flow rate = 0.65 kg/s.
Temperature of hot gasses entering exchanger = 870°C.
Temperature of cold air entering exchanger = 40°C.
Both gases are approximately at atmospheric pressure.
GIVEN
? The crossflow tube bank heat exchanger shown above
? Air flow rate
( ma ) = 0.4 kg/s
? Gas flow rate
( mg) = 0.65 kg/s
? Entrance temperatures
? Air (Ta,in) = 40°C
? Gas (Tg,in) = 870°C
? Both gases are at 1 atm pressure
FIND
(a) The overall heat transfer coefficient
(b) The rate of heat transfer (q)
ASSUMPTIONS
? The hot gases have the same thermal properties as air
? No scaling
? Thermal resistance of the tube walls can be neglected
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
From Appendix 2, Table 28, for dry air at the entering temperatures