Refer to the diagram where D and S are the United States' demand for and supply of Swiss francs. At the equilibrium exchange rate, E, the United States' balance of payments is in equilibrium. Under a system of fixed exchange rates, the shift in demand from D to D' will cause:
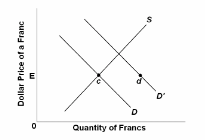
A. the United States to increase its stocks of international monetary reserves.
B. a Swiss balance of payments deficit.
C. a U.S. balance of payments deficit.
D. a U.S. balance of payments surplus.
C. a U.S. balance of payments deficit.
You might also like to view...
The cultural hypothesis of economic growth claims that:
A) most of the ancient cultures of the world have almost been forgotten post-globalization. B) different values and cultural beliefs cause differences in prosperity around the world. C) a common global culture is automatically created through liberal trade practices. D) values and cultural beliefs are proximate causes for differences in prosperity around the world.
Over the past century in the United States, real GDP per person has grown, on average, by about
a. 1 percent per year. b. 2 percent per year. c. 3 percent per year. d. 5 percent per year.
Assume initially that the price of X (measured on the horizontal axis) is $9 and the price of Y (measured on the vertical axis) is $4. If the price of X now declines to $6, the budget line will:
A. be unaffected. B. shift outward on the vertical axis. C. shift inward on the horizontal axis. D. shift outward on the horizontal axis.
One key implication of rational expectations is that
A. anticipated monetary policy cannot affect the level of real Gross Domestic Product (GDP). B. anticipated monetary policy has no effect on the price level. C. both unanticipated monetary policy and anticipated monetary policy have an effect on the economy. D. unanticipated monetary policy has no effect on the economy but anticipated monetary policy does have an effect on the economy.