A 5-year plan to raise extra funds for public schools involves an “enrichment tax” that will raise $56 for every student the first year, increasing by $1 per student per year thereafter. There are 50,000 students in the district in year one, 51,000 in year 2, with increases of 1000 students per year thereafter. Calculate the future worth in year 5 of the enrichment plan over a 5-year planning period at an interest rate of 8% per year. Solve this problem using (a) tabulated factors, and (b) a spreadsheet.
What will be an ideal response?
(a) Using factors, determine the annual cash flow with arithmetic gradient values of G tax =
$1 for the tax and G stu = 1000 for students. The resulting cash flows do not form an
arithmetic gradient series.
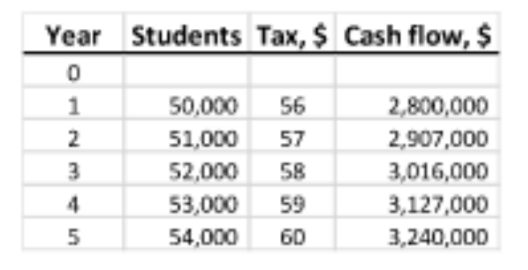
P = 2,800,000(P/F,8%,1) + 2,907,000(P/F,8%,2) + … + 3,240,000(P/F,8%,5)
= 2,800,000(0.9259) + 2,907,000(0.8573) + … + 3,240,000(0.6806)
= $11,982,281
F = 11,982,281(F/P,8%,5)
= 11,982,281(1.4693)
= $17,605,565
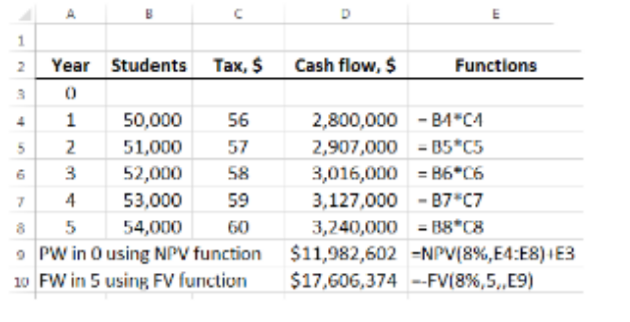
(b) Spreadsheet solution
You might also like to view...
When a country's quantity supplied exceeds its quantity demanded for any given price, then this indicates the country has
A) Excess supply. B) Import demand. C) Excess demand. D) None of the above
Is the permeability of a material for air the same as its permeability for water vapor? Name some building materials that are impermeable to both air and water vapor.
What will be an ideal response?
Most engineering drawings include three views:
A. Top, front, and left-side B. Top, front, and bottom C. Front, right-side, and left-side D. Top, front, and right side
What is tropospheric ozone and why are we not concerned with protecting it?
What will be an ideal response?