Compare and contrast hormones, neurotransmitters, and neurohormones.
What will be an ideal response?
See Figure 6.1 and the "Long-Distance Communication May Be Electrical or Chemical" section in the chapter.
You might also like to view...
Why are you able to repeatedly contract and relax your muscles of respiration, allowing you to breathe in and breathe out?
a. As soon as all of the Ca2+ stored in the lateral sacs of the sarcoplasmic reticulum is used up, muscle relaxation occurs. b. After the muscle cell becomes excited, acetylcholinesterase rapidly destroys acetylcholine. c. When there is no longer a local action potential in the muscle cell, Ca2+ is actively transported back into the lateral sacs of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and muscle relaxation occurs. d. Both (b) and (c) above. e. All of these answers.
The deepest meningeal layer that is tightly attached to the spinal cord is called the ____ ___.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word.
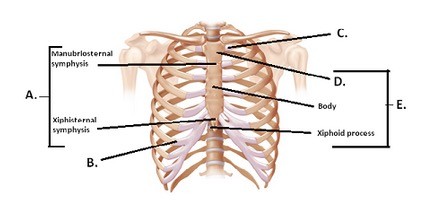 The figure illustrates the joints and bones of the rib cage. What does "C" represent?
The figure illustrates the joints and bones of the rib cage. What does "C" represent?
A. Costochondral joint B. Sternum C. Sternocostal synchrondrosis D. Manubrium E. Sternal symphyses
The metacarpophalangeal joints at the base of the fingers are ________ joints.
A. pivot B. hinge C. condylar D. plane (gliding) E. ball-and-socket