Nonexcludable goods tend to be undersupplied because:
A. the free rider problem persists.
B. people do not pay the true value of the good.
C. people rarely willingly pay for something they could get for free, regardless of how much they value it.
D. All of these statements are true.
D. All of these statements are true.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 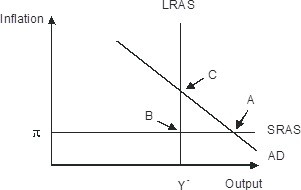
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Marginal cost is the change in the:
A) total cost associated with producing one more unit of output. B) average total cost associated with producing one more unit of output C) average variable cost associated with producing one more unit of output. D) opportunity cost associated with producing one more unit of output.
Most economists agree that the economy will adjust to a recessionary gap, but the adjustment process
a. is rapid and destabilizing. b. is moderately quick, but not as rapid as necessary. c. takes place solely on the supply side. d. is very slow.
Which of the following is true?
A. Frictional unemployment implies a lack of available jobs. B. During a recession, cyclical unemployment will be low. C. When an economy is at full employment, actual unemployment will be less than the natural rate of unemployment. D. When actual GDP equals potential GDP, the actual unemployment rate will equal the economy's natural rate of unemployment.