An example of automatic fiscal policy is
A) an interest rate cut, initiated by an act of Congress.
B) an increase in the quantity of money.
C) a tax cut, initiated by an act of Congress.
D) a decrease in tax revenues, triggered by the state of the economy.
E) any change in the interest rate, regardless of its cause.
D
You might also like to view...
A decrease in the discount rate will
A) have an unclear effect on the money supply. B) decrease the money supply. C) increase the money supply. D) not affect the money supply.
A productivity improvement will cause
A) a rightward movement along the saving-per-worker curve and an increase in the capital—labor ratio. B) an upward shift in the saving-per-worker curve and an increase in the capital—labor ratio. C) a downward shift in the saving-per-worker curve and a decrease in the capital—labor ratio. D) a leftward movement along the saving-per-worker curve and a decrease in the capital—labor ratio.
When economists look at the percentage change in quantity demanded for air travel generated by a change in income, they are looking at the
a. price elasticity of demand for air travel b. income elasticity of demand for air travel c. price elasticity of demand for airline tickets d. cross elasticity of demand for airline tickets e. cross elasticity of demand for airline travel
Refer to the graph shown. Expansionary fiscal policy is most likely to shift the aggregate demand curve from: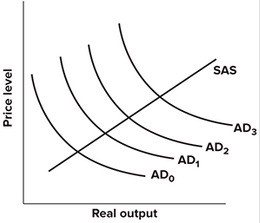
A. AD0 to AD2 if crowding out does not occur and from AD0 to AD3 if crowding out does occur. B. AD2 to AD0 if crowding out does not occur and from AD1 to AD3 if crowding out does occur. C. AD0 to AD2 if crowding out does not occur and from AD0 to AD1 if crowding out does occur. D. AD2 to AD0 if crowding out does not occur and from AD1 to AD2 if crowding out does occur.