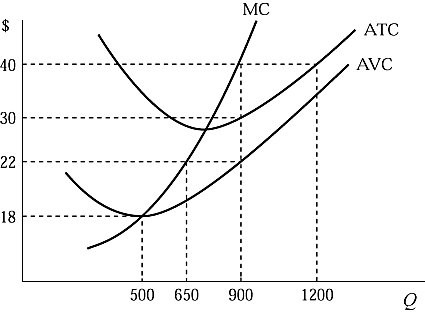
 Figure 6.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit-maximizing output level, its total variable cost is:
Figure 6.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit-maximizing output level, its total variable cost is:
A. $12,500.
B. $14,300.
C. $19,800.
D. $27,000.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 11.2. Assume the economy is in equilibrium at 1, where real GDP equals potential GDP, and then the economy experiences a positive demand shock. Other things equal, the positive demand shock is best represented by a(n)
A) movement up along the Phillips curve. B) movement down along the Phillips curve. C) upward shift of the Phillips curve. D) downward shift of the Phillips curve.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1) Uncertainty is the result of incomplete information. 2) Probability is the chance that an event occurs. 3) It is possible for the probability of an event to be 1.50. 4) A probability distribution of a random variable is a listing of all of the possible outcomes of the random variable and the associated probabilities. 5) The larger the extent of variation, the smaller the risk.
The long run outcome of the monopolistically competitive firm:
A. is not efficient. B. does not maximize profits. C. is the same as the short-run outcome. D. maximizes total surplus.
Is it possible for a country to experience a permanent increase in output per worker over time? If so, how can this occur?
What will be an ideal response?