The efficiency
A) gain from a fixed exchange rate with the euro is smaller when trade between say, Norway and the euro zone, is extensive than when it is small.
B) gain from a fixed exchange rate with euro is greater when trade between say, Norway and the euro zone, is extensive than when it is small.
C) loss from a fixed exchange rate with the euro is smaller when trade between say, Norway and the euro zone, is extensive than when it is small.
D) gain from a fixed exchange rate with euro is the same as when trade between say, Norway and the euro zone, is extensive than when it is small.
E) gain from a fixed exchange rate with euro is the same as when trade between say, Norway and the euro zone, is small than when it is small.
B
You might also like to view...
Under a fixed exchange rate system, a balance of payments deficit may:
A) decrease the country's money supply if there is a non-sterilized central bank intervention. B) decrease the country's money supply if there is a sterilized central bank intervention. C) increase the country's money supply if there is a non-sterilized central bank intervention. D) increase the country's money supply if there is a sterilized central bank intervention.
As a tax increases, the excess burden from increasing the tax grows faster than the corresponding tax revenue. This is the impetus behind _____
a. lump sum taxes b. the excess burden rule c. the Ramsey rule d. placing taxes only on the most inelastic goods
Something is valuable if:
A. it does not involve a trade-off. B. it is a good or a service. C. someone wants it. D. it was made using resources.
If Don has budget constraint C in the graph shown, what is the trade-off he faces in terms of the two goods?
This graph shows three different budget constraints: A, B, and C.
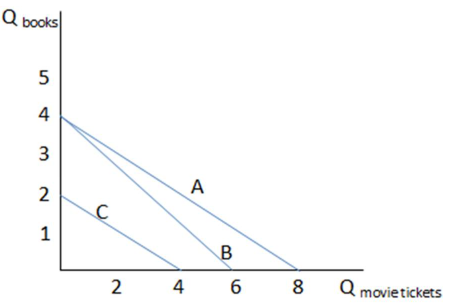
A. Two cases of soda for every three gallons of milk
B. One case of soda for every one and a half gallons of milk
C. Three cases of soda for every four and a half gallons of milk
D. All of these accurately reflect Don's tradeoff.