Refer to the table below. Busy Betty sells her cakes for $20 each and her constant marginal cost to produce each cake is $12, which is equal to her (constant) average total cost. If she does not sell a cake the day she makes it, she sells it as day-old cake for $10. What is her expected marginal cost of holding the 20th cake in inventory?
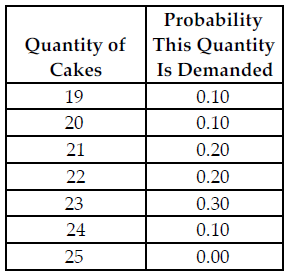
The above table shows the probability distribution of cake sales at Busy Betty's Bakery.
A) $0.40
B) $10.00
C) $0.20
D) $2.00
C) $0.20
You might also like to view...
Migration from poor to rich countries hurts poor countries through
a. loss of educated individuals b. residents sending money abroad to migrants c. tightening job markets at home d. opening executive jobs to workers from developed countries e. all of the above
An increase in all of the following will increase aggregate demand EXCEPT
A) investment. B) savings. C) exports. D) government spending.
Watt Power and Light, an electric company, will suffer an economic loss
a. even at its profit-maximizing output because marginal cost is always less than average cost b. even at its profit-maximizing output because average cost is always less than marginal cost c. if regulators insist that it produce where price equals marginal cost because marginal cost is less than average cost d. if regulators insist that it produce where price equals marginal cost because average cost is always less than marginal cost e. if regulators insist that it produce where price equals average cost because average cost is always less than marginal cost
Eurozone countries:
a. have no separate legal tender. b. are pegged to the euro. c. are pegged to the dollar. d. are fixed against a single currency