The intensity of sunlight falling on the earth is about 1.4 kW/m2 (before any gets absorbed by our atmosphere). At what rate does the sun emit light energy? (The earth-sun distance = 1.5 × 108 km and the earth's radius = 6.4 × 103 km.)
A) 4.0 × 1026 W
B) 3.2 × 1022 W
C) 7.2 × 1014 W
D) 7.6 × 108 W
A
You might also like to view...
Length Contraction: A stretch of land is 12.5 km long on a map.(a) What would be its length to an observer moving by, parallel to the stretch, at 0.9500c?(b) Which is the proper length for this stretch of land?(c) How fast relative to Earth would the observer have to move for the land to appear 6.50 km long? Express your answer in terms of the speed of light.
What will be an ideal response?
An object’s x-acceleration ax (t) is shown in the boxed graph at the top left. Which of the other graphs in the set most correctly describes its x-velocity?
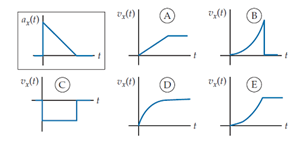
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
The CFC propellants used in aerosol cans are chemically inert gases. This inertness leads to problems with stratospheric ozone because
A) inert gases do not travel far in the atmosphere, so they are likely to react before rising very high. B) inert gases are especially likely to react chemically with the atmosphere. C) inert gases can drift upward for great distances without being broken down by the atmosphere. D) inert gases are especially attracted to ozone due to the fact that ozone is so highly reactive. E) inert gases are especially attracted to other inert, or nonreactive, gases such as ozone.
The accelerating force of the wind on a small 300-kg sailboat is 780 N northeast. If the drag of the keel is 552 N acting west, what is the acceleration of the boat?
a. 4.4 m/s2 due east b. 1.8 m/s2 due north c. 2.6 m/s2 northeast d. 3.2 m/s2 north by northwest e. 0.23 m/s2 due east