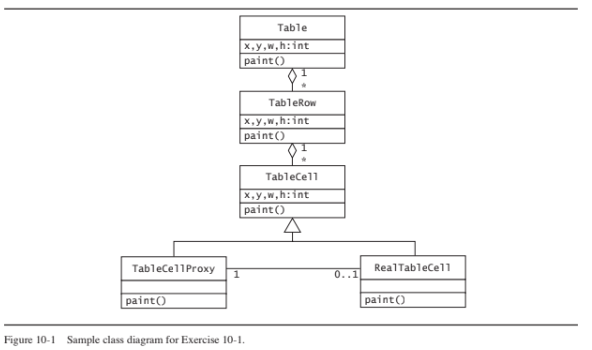
In Web pages, tables consist of rows, which in turn consist of cells. The actual width and height of each cell is computed based in part on its content (e.g., the amount of text in the cell, the size of an image in the cell), and the height of a row is the maximum of the heights of all cells in the row. Consequently, the final layout of a table in a Web page can only be computed once the content of each cell has been retrieved from the Internet. Using the proxy pattern described in Figure 10-7, describe an object model and an algorithm that would enable a Web browser to start displaying a table before the size of all cells is known, possibly redrawing the table as the content of each cell is downloaded.
What will be an ideal response?
The proxy design pattern is applied to the table cell. When created, TableCellProxy estimates its dimensions as best
as it can and updates them as the content is retrieved. Every time TableCellProxy provides a new estimate of its
dimensions, it signals Table (e.g., via a semaphore or a listener). The Table then recomputes the dimensions and
positions of all of its rows and redraws itself.
In general, the challenge of this type of approach is not the algorithm but to provide a visual behavior that does not
confuse the user, especially when only part of the table is visible.
You might also like to view...
Assume that t is an object of class Test, which has member functions a(), b(), c() and d(). If the functions a(), b() and c() all return references to an object of class Test (using the dereferenced this pointer) and function d() returns void, which of the following statements will not produce a syntax error:
a. t.a().b().d(); b. a().b().t; c. t.d().c(); d. t.a().t.d();
Bound forms can be used to specify parameters, create buttons to print reports, provide navigation menus, and other similar operations
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The Bring to Front command is found on the Arrange menu.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
__________ is the term used for a set of rules that must be strictly followed when writing a program.
a. Semantics b. Syntax c. Grammar d. Key words