How do prices in monopolistically competitive firms compare to those in perfect competition?
What will be an ideal response?
Ans: They would be slightly higher because the affected firms do have the power to raise prices, but given the number of firms and ease of entry, prices would not increase as much as they would in the case of a true monopoly.
You might also like to view...
If there is unplanned inventory decumulation there is excess
A) demand for bonds. B) supply of bonds. C) demand for commodities. D) supply of commodities.
Commitment devices are:
A. methods to increase the price of your vices. B. methods to lower the price of your virtues. C. successful whether weak or strong, depending on the situation. D. All of these statements are true.
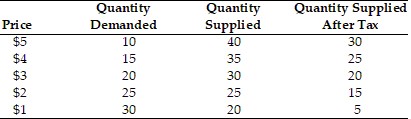 The demand and supply of a product is given in the above table. A unit tax of $2 is imposed on the product. The equilibrium quantity for this product after the tax is imposed is equal to
The demand and supply of a product is given in the above table. A unit tax of $2 is imposed on the product. The equilibrium quantity for this product after the tax is imposed is equal to
A. 25 units. B. 30 units. C. 15 units. D. 20 units.
A market situation in which a large number of firms produce similar but not identical products is
A. an oligopoly. B. a monopoly. C. monopolistic competition. D. perfect competition.